What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? An Enterprise Guide.
Robotic process automation (RPA) is software technology for quickly and reliably automating digital tasks. RPA remains a core technology for enabling enterprise automation, working alongside AI tools including generative AI, to execute business processes with speed and accuracy at scale.
Types of RPA
A method of business process automation, RPA employs software robots, or "bots," to automate digital tasks typically performed by humans. RPA is known for its reliability in automating high-volume, repetitive tasks such as data extraction, form filling, copy-pasting, making calculations, file transfers, and connecting to APIs. Working via user interfaces as well as APIs, RPA integrates and executes processes and tasks across applications, including legacy enterprise systems.
One of its defining features is its simplicity to use. Configuring RPA-driven workflows does not require software development or coding skills—if you know how to record video on your phone, you’ll be able to set up automations with RPA.
While just as straightforward and intuitive to use, enterprise-level RPA is also designed for the security, systems integration, scale, and compliance requirements of large organizations. Robust and resilient, enterprise RPA is capable of orchestrating thousands of automations at the same time while ensuring high availability and performance across operations.
It’s important to note that RPA on its own is not an application of artificial intelligence (AI). RPA is purely process-driven, following only predefined workflows to replicate human-driven tasks.
However, enterprise RPA deployments typically harness AI to work in tandem with RPA, expanding automation capabilities to more complex use cases, delivering deeper insights, and accelerating process discovery and automation development.
Attended RPA is used to assist human workers with routine tasks. This form of RPA depends on triggers or inputs to initiate specific automated tasks. Attended RPA bots are designed to work alongside human users, providing real-time assistance for interactive business processes such as in customer service and IT helpdesk operations.
Unattended RPA, as the name implies, operates without human intervention. These automations run independently based on pre-programmed triggers, data inputs, and schedules. Unattended RPA is most often applied to so-called back-office processes like data entry, IT processes, and application integrations.
Hybrid RPA is a blend of both attended and unattended RPA, where bots and human workers can interact and collaborate on tasks and processes. More adaptive to the realities of complex business processes, hybrid RPA workflows enable the speed and efficiency of automated execution in combination with human decision-making.
Benefits of RPA.
RPA has a positive snowball effect on business operations; it delivers measurable business benefits right out of the gate—think cost reduction, greater accuracy, delivery speed—then continues to add value as it picks up transformational momentum and increases productivity across the organization.
Greater security and scalability
RPA is a fast, inexpensive way to achieve business process automation at scale with complete adherence to security and compliance requirements. In fact, RPA can be used to strengthen IT security by deploying automations that protect sensitive data and eliminate risks associated with human error. RPA enables high-volume business processes to be more elastic, able to handle any workload—planned or unplanned—in real time whenever required.
Productivity and digital transformation
In concert with AI technologies, RPA plays an important role in digital transformation efforts. RPA delivers productivity gains from the speed, reliability, and precision of RPA execution at the same time as it enables employee time to be used toward strategic, higher-value activities.
Process and cost efficiencies
RPA is application agnostic and unfettered by technology silos, able to seamlessly connect between software tools regardless of function and department. That means RPA does not require any changes to underlying systems and can integrate and operate across environments and applications to achieve enterprise-wide efficiencies and deliver lower operating costs.
Guaranteed compliance
RPA can adhere to strict compliance standards, performing tasks and processes exactly as prescribed each and every time—and generating a complete, detailed audit trail of every action. Automating with RPA is enabling industries such as finance, healthcare, and life sciences to guarantee compliance and protect sensitive data at all times.
Improvements in employee experience
RPA frees human workers to focus on rewarding, fulfilling, and valuable work like solving problems, making decisions, and building relationships.
Enterprise use cases for RPA.
RPA excels at executing manual and repetitive tasks like billing and coding invoices in finance or sending appointment reminders in healthcare delivery settings. For enterprises in nearly every industry, applying RPA to automate time-consuming workflows such as data entry, customer service responses, report generation, and even email management, has proven to be a game changer, delivering dramatic time and cost savings and freeing employees for strategic work.
Extending RPA with AI tools further ups the ante, enabling the automation of more complex tasks and workflows for increasing transformational value and ROI.
Financial Services
Financial services processes are prime candidates for the accuracy, security, and compliance gains offered by automating with RPA. Tasks to automate with RPA include customer onboarding, where it can speed up collecting and verifying customer information, cutting processing time and improving customer experience.
RPA is also excellent for automating loan processing, able to handle data entry and document checks for credit assessments, supporting faster decisions with higher accuracy. In the case of mortgage quality checks, for KeyBank, RPA contributed to completing nine years of work in the span of two weeks. In compliance and regulatory reporting, RPA can help by gathering and processing data to reduce the chance of human error and verify that requirements are met.
Healthcare
RPA can inject operational efficiency into healthcare processes, reducing administrative burden and enabling personalized patient care to ultimately improve outcomes. For one UK hospital network, implementing RPA saved 7,000 hours per year.
Top RPA use cases in healthcare include patient scheduling, where RPA can automate appointment bookings, reminders, and cancellations to improve patient access and drive down no-show rates. Applying RPA is also valuable to accelerate claims processing and shorten shorten reimbursement cycles by automating the verification of patient information, claims submissions, and tracking follow-ups.
Another significant RPA use case in healthcare is patient data management. RPA can extract and input data from multiple sources to update and validate information within electronic health records (EHR). In addition, RPA can boost compliance and regulatory reporting by automating data collection and analysis to meet regulatory requirements and minimize errors.
Manufacturing
From factory floor to back office, applying RPA to use cases throughout manufacturing operations can reduce costs, improve productivity, and speed up time-to-market. Practical use cases for RPA in manufacturing include inventory management, where RPA can automate stock level monitoring, reorder processes, and inventory reconciliation, ensuring optimal stock levels and reducing the risk of shortages or overstock.
Another opportunity to apply RPA is order processing. RPA can automate handling purchase orders, invoices, and shipment tracking, improving accuracy and fulfillment times—for Stant, RPA enabled 80% straight-through invoice processing.
RPA can also automate data collection and analysis for product inspections to help ensure compliance with quality standards. And RPA can assist with maintenance management by automating the scheduling of preventive maintenance tasks and tracking equipment performance data, contributing to reduced downtime and operational continuity.
Customer Service
RPA answers the call in customer service to simultaneously increase operational efficiency and delight customers. A common use case for RPA in enterprise customer service environments is automating inquiry handling through chatbots or virtual assistants that employ RPA to respond to routine questions either directly, in straightforward cases such as requests for order status or account information, or by quickly directing more complex inquiries to the right agents. Another application use case is ticketing and issue resolution. RPA can log customer complaints, categorize, and route them to support teams, helping to reduce response times.
New customer onboarding is a natural match for RPA to automate data entry and verification to deliver a faster, smoother customer experience, that can be nearly impossible without RPA. And RPA can manage feedback and surveys, automating customer feedback collection and analysis, driving a faster feedback-improvement loop.
How RPA fits into enterprise automation initiatives.
To build or manage an enterprise-wide automation program, it's important to recognize that RPA is not a stand-alone solution. For automations that effectively collaborate with human teams, integrate seamlessly with enterprise systems, and manage significant workloads, RPA must be part of a comprehensive AI-driven automation strategy that addresses the complexity and scale of interactive business processes and interconnected global operations.
However, RPA remains integral to enterprise automation, serving as the core mechanism to accomplish automated work alongside pre-built integrations and API connectors. It acts as the "arms and legs" of automation within a larger AI-driven automation framework that powers uncovering workflows, developing automations, and sourcing the necessary data to drive automated operations.
In short, a robust enterprise automation solution incorporates RPA as a key component of a holistic AI + automation system that addresses the entire automation lifecycle, from process discovery to program management and expansion.
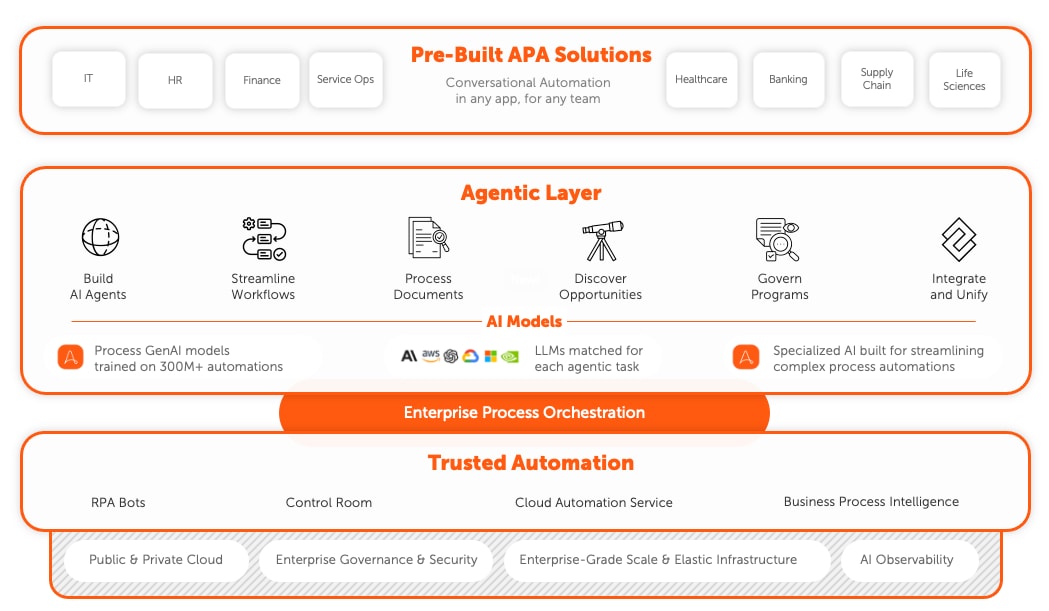
AI and RPA: How AI is changing enterprise automation.
RPA has come a long way in a short time. By automating repetitive, high-volume tasks like data entry, scraping, and extraction with low-code, easy-to-adopt automation tools, RPA broke down long-standing productivity barriers.
This RPA-led foundation for enterprise automation became the springboard for Intelligent Automation, combining RPA with cognitive technologies, such as machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, fuzzy logic—and, most recently, generative AI.
Generative AI has already revolutionized enterprise automation capabilities, powering faster, easier automation development and interaction. Infusing Intelligent Automation platforms with generative AI has enabled natural language automation assistance, auto-generation of functional automations that accelerate the automation development lifecycle, and resilient, self-healing automations that can auto-recover from changes to underlying applications (formerly the Achilles’ heel of RPA-driven automations), cutting execution failures by over 50%.
Generative AI is also the engine of AI agents, a significant technology advancement harnessing the cognitive capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to make decisions, learn from data, interact with humans through natural language, and ultimately take action to achieve goals. Enabling action requires connecting AI agents with applications and systems where they can get work done, such as sending an email or saving a report. At the process level, agentic workflows can choose RPA bots to accurately execute tasks.
In fact, platforms to deliver Intelligent Automation solutions through RPA and AI are proving to be the path for building, deploying, and managing AI agents for enterprises. Architected for enterprise security at all levels from handling data sources to application access controls, RPA and AI automation platforms are ready for the security, privacy, and governance complexities of enterprise deployments. They are also built to scale—already orchestrating thousands of automations with central management and oversight.
Embedded into agentic workflows, AI agents are poised to change the face of enterprise automation. Forrester research points out several ways they can be applied today—either replacing RPA within existing automated workflows, working in tandem with RPA, or connecting with other AI agents to perform end-to-end processes as part of multi-agent systems.
How to deploy RPA in the enterprise.
Organizations on the journey to successful automation deployment have a wealth of resources and expertise to draw from and a growing list of best practices gleaned from standout RPA implementations by both industry analysts and solution providers. What’s on the short list of considerations for bringing an automation strategy to life with RPA?
Initiate change by engaging stakeholders right from the start.
Put human workforce needs at the center of planning, bring in HR early and involve a broad cross-section of stakeholders, leaders who can influence change, and automation champions. Diverse input will help shape a robust and inclusive strategy, so ask lots of questions—both internally and externally; reach out to trusted partners, vendors, and other organizations already on the RPA journey.
Build a solid foundation by establishing a center for RPA standards and oversight.
Start strong by creating an organization-wide center of excellence (CoE). The CoE should focus on effectiveness and governance, and will be in charge of creating standards to ensure compliance, security, and continuous improvement across the automation life cycle. It’s a hub of expertise, established to help the entire organization get up and running with consistent, high-quality automations by propagating best practices, tools, and templates.
Select a vendor by evaluating your best-fit solution and support model.
Choose a vendor that aligns with your long-term automation and business goals. RPA's success hinges on workforce adoption, which means selecting software that is both technically robust and user-friendly for all employees, not just IT specialists.
Pricing model: Transparent cost structures help you avoid unexpected expenses as your RPA deployment scales. Look for flexibility in pricing, including options for unlimited bot usage.
Innovation: The landscape of RPA technology is rapidly evolving. Look for vendors with proven experience and stability who are committed to continuous innovation. Prioritize vendors with dedicated teams focused on enhancing RPA capabilities, including migration tools, orchestration, and AI integration.
Support: Robust customer support, comprehensive training programs, and active community engagement will support a successful automation journey.
Security: One of the core benefits of RPA is strengthening security, which relies on the security architecture and certifications a solution adheres to. If relevant, consider vendors that offer vertical-specific solutions for industries with stringent data security requirements, such as government, financial services, and healthcare.
Flexibility: It's important to select solutions that enable both attended and unattended automation, providing flexibility in task execution. The RPA solution should integrate seamlessly with existing systems, including legacy applications and cloud services. Choose vendors that invest in AI-driven features to improve automation efficiency and adaptability.
Accessibility: Consider platforms that offer low-code or no-code development options, allowing both technical and non-technical users to easily create and use automations. Look for training and tools for citizen developers that maintain IT oversight to ensure quality and security.
Scale: Design automation with growth in mind. Even if you start with small pilots, ensure that platform infrastructure, licenses, and governance frameworks can adapt as your automation needs expand. Look for solutions that can dynamically scale to accommodate increasing workloads and user demands without compromising performance.
Start automating by aligning RPA with business goals and workforce needs.
Determine which processes will yield the greatest ROI through automation. Many organizations choose to start small, automating tasks that are part of a larger process. RPA applied in this way is referred to as attended automation; it has the benefit of allowing your workforce to become familiar with RPA firsthand, as it takes on a repetitive segment of a pre-existing workflow, remaining closely supervised.
On the other hand, successful enterprise automation deployments take an all-encompassing approach to implementation, redesigning processes from scratch to fully incorporate automation tools and gain maximum value right out of the gate.
Measure effectiveness with a system of KPIs and analytics.
Track bot performance, uptime, and ROI, and use this data to optimize processes and refine automation strategies. Ensure the solution includes management features for monitoring, configuration, and governance of automated processes. Regularly gather feedback from users and stakeholders to refine automations and address opportunities and challenges that arise post-deployment.
Challenges and considerations for deploying RPA solutions.
Implementing RPA solutions will present a set of challenges and considerations that reflect the unique operating environment of each organization. Thoroughly assessing business needs and barriers and proactively sharing insights as part of both vendor selection and while developing automations can help ensure a successful path to RPA deployment.
Difficulty discovering processes
Organizations often struggle to identify and map out existing processes accurately, leading to missed automation opportunities. This can easily be overcome by selecting an RPA platform with integrated AI tools for discovering and documenting processes.
Inefficient process optimization
Closely related to challenges in process discovery, organizations can face hurdles to optimizing workflows due to a lack of clear visibility into how tasks are performed and where bottlenecks occur. This can be alleviated by implementing a solution with built-in process visualization.
Need for data structuring
On their own, processes automated with RPA require pre-structured data to function. However, most data is not ready for its close-up, as most business information resides in unstructured formats like emails and documents. Integrated document automation tools can solve for the data structuring needs of automated workflows by sourcing, extracting, and delivering the right data at the right time.
Insufficient governance
A lack of governance models can lead to inconsistencies in automation practices which can undercut scaling efforts. Effective governance ensures the reliability, compliance, and operational effectiveness of automation programs, supporting scale and helping to protect organizations and their customers from exposure to risks like disruptions or data breaches.
Maintaining automations
Organizations may not have enough skilled personnel to maintain automations. UI-based automations will fail when the source application interfaces change due to updates, leading to days of potential downtime and resources needed to search for the change to update the automation. However, new tools are available that use generative AI to identify the change and update the automation in real-time.
The RPA landscape: High-level overview
Automation technology is a fast-moving market. AI-driven advancements and speciality solutions have pushed rapid proliferation of vendors and features. At the same time, several enterprise solutions have maintained consistent market leadership, with Automation Anywhere for example appearing for six consecutive years in the Leader quadrant of Gartner’s annual RPA market report. The 2024 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Automation is a valuable companion to building a complete understanding of the RPA vendor landscape.
Enterprise solutions
These include Automation Anywhere and UiPath. These vendors are specifically designed for enterprise requirements, featuring extensive integrations and partner ecosystems, robust training programs, and the scalability to support enterprise use cases. Importantly, enterprise solutions include powerful AI capabilities that recruit the execution strengths of RPA to help automate complex, dynamic business processes.
Ecosystem-based solutions
These include ServiceNow, Salesforce, and SAP. These vendors offer tools purpose-built to integrate with their own ecosystems, making them less suitable as standalone solutions, and with less comprehensive offerings compared to enterprise solutions.
Speciality solutions
These include IBM and Nintex. These vendors tend to focus on specific regions and their solutions center around workflow automation. They may have notable feature gaps compared to enterprise solutions, often lacking essential pieces for enterprise deployments such as compliance support or a marketplace for development tools.