The benefits of automation software.
Automating business processes saves time, reduces errors, and increases efficiency. Automation software provides the means to transform the way businesses operate by streamlining and automating processes, reducing human error, and freeing up valuable resources for more strategic initiatives.
Accuracy
Automating repetitive processes ensures a level of accuracy that is hard to attain with human execution. Higher accuracy, in turn, drives better quality through repeated error-free processes and outcomes.
Compliance
Automated processes are consistent across each and every execution, which means the process will comply with all requirements as it was designed. In addition, automation software can be used to continuously monitor and ensure compliance with applicable regulations and standards.
Reduced costs
Automating processes delivers cost savings through error reduction, efficient use of resources, time savings, and, for cloud automation software, lower infrastructure costs. In addition, automation can contribute to sustainability by optimizing resource usage and reducing waste.
Process improvement
Implementing automation software drives process improvement by helping to uncover existing processes and streamline complex workflows, eliminating bottlenecks and reducing the need for human intervention.
Capacity scaling
Easily handle increased workloads without proportional increases in human resources. Automating processes typically offers built-in scalability to fit business needs. And, scaling automated processes maintains accuracy and efficiency, supporting accelerated production and overall operations.
Higher employee satisfaction
As a tool to execute mundane, time-consuming, and repetitive tasks, automation software can improve the employee experience, alleviating monotonous tasks so employees can spend more time on creative, strategic, and problem-solving activities, which can lead to higher job satisfaction and reduced burnout.
Better customer experiences
By automating customer support tasks, enterprises can provide faster and more reliable service with quicker response times while enabling more personalized and timely customer interactions, helping to build stronger customer relationships.
Faster decision-making
Automation software can generate reports and dashboards that provide a clear overview of business KPIs. Able to process both large volumes of data in real time as well as consolidate multiple data sources (e.g., CRM, ERP, HRM), automation software delivers centralized access operational data, supporting rapid response to changing market conditions, customer needs, and operational challenges.
Types of automation software.
Automation software can encompass business operations or focus on stand-alone tasks and processes. Many automation tools target processes in specific functions or departments, offering process templates and feature sets to address related use cases or process areas such as finance and accounting, email marketing and lead capture, or integrations.
At the other end of the spectrum, enterprise automation software casts a much wider net across operations and teams to enable the automation of any business process. Enterprise automation solutions provide robust capabilities to connect tasks and processes across functional areas, automate entire workflows, and eliminate operational silos.
Across automation software types you will find different combinations of automation technologies from core execution tools like optical character recognition (OCR) and robotic process automation (RPA) to advanced capabilities integrating artificial intelligence (AI) such as intelligent document processing (IDP), Intelligent Automation, and agentic automation.
Optical character recognition (OCR)
OCR is a technology that transforms images of text into machine-readable, searchable data and is typically used in business workflows that involve high volumes of paperwork, such as invoices, receipts, and legal documents. OCR technology also plays an integral role within advanced data processing automation solutions across industries, from scanning number plates in self-driving cars to digitizing patient records in healthcare settings, providing valuable information for operational decisions.
Self-serve automation
Self-service automation software is a centrally-managed automation platform that is typically managed by IT to give teams in other departments simple, secure tools to use automation at work. The software allows users to trigger automated business processes as well as cancel and restart them while providing IT with continuous monitoring. This kind of automation software can help non-technical teams, such as sales, marketing, and HR, to create and run automated jobs without requiring coding or visual workflow editing expertise.
Low-code / no-code automation
No-code automation software, as its name implies, allows users to automate tasks and workflows without coding experience. Its major distinction from other automation tools is in its visual drag-and-drop user experience with predefined actions to simplify process building and customization, making automation accessible to employees and citizen developers outside of IT or automation teams. Enterprise automation software typically includes no-code automation features, often supported by generative AI-powered assistants, while stand-alone no-code automation platforms such as Zapier and Hubspot usually focus on offering out-of-the-box solutions tailored to specific departments, including HR, IT, procurement, and project management.
Intelligent document processing (IDP)
IDP uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with optical character recognition (OCR) to extract, classify, and organize data from business documents. IDP not only recognizes and extracts data from documents but also interprets the context and meaning of the information. IDP tools can quickly transform large volumes of unstructured and semi-structured documents into accessible and usable information. Typically, IDP is used in combination with Intelligent Automation to power end-to-end process automation. Common use cases include automating loan applications, digitizing patient records or insurance claims, invoice processing, and employee onboarding.
Robotic process automation (RPA)
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a type of automation technology that uses software programs, often referred to as 'bots', to perform repetitive, rule-based digital tasks at high volume and speed. Unlike other automation tools, RPA mimics human interactions with systems and applications to perform repetitive tasks such as data scraping, making calculations, opening and moving files, and logging into programs. RPA excels at work that requires repeated precision and 100% accuracy, such as data entry and invoice processing. While RPA can function independently for structured data tasks, it is often one part of an Intelligent Automation platform, where it is integrated with AI tools for handling unstructured data, providing a more comprehensive automation solution.
Business process automation (BPA)
BPA software is an automation technology that combines software solutions to automate multi-step business processes. BPA concentrates on more complex enterprise processes that often touch multiple IT systems, tailoring each automation to meet the specific needs of an organization. BPA is typically applied where processes require coordinating multiple systems, such as fulfilling and invoicing a customer purchase order, approving a loan application, or onboarding a new employee.
Intelligent Automation
Intelligent Automation is an advanced level of automation technology, integrating AI and technologies such as machine learning (ML) and RPA. Compared to standard automation tools that require well-defined, preset rules and structured inputs, Intelligent Automation uses AI's cognitive capabilities to understand, learn, and make informed decisions based on ambiguous or unstructured data, expanding the possibilities of business process automation. Intelligent Automation is used across industries to automate complex business processes and transform operations. Applicable to any digital business process, Intelligent Automation can process and predict complex data, improve data capture and retrieval, enhance accuracy and response times and strengthen security and compliance standards.
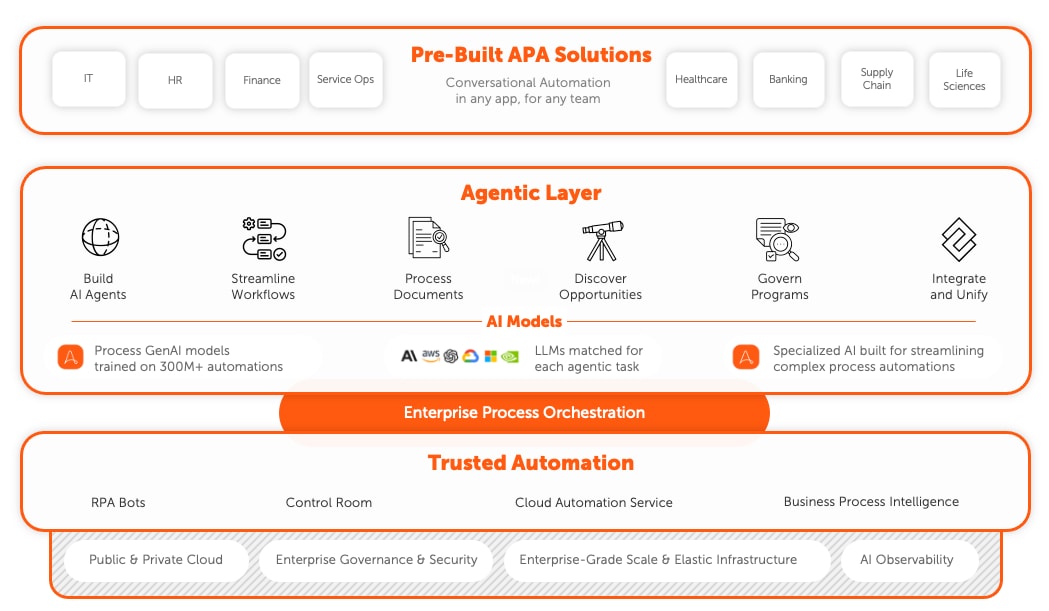
Agentic automation
Agentic automation, also called agentic process automation (APA), harnesses the potential of large language models (LLMs) to complete complex tasks requiring human-like intelligence. Distinct from traditional robotic process automation (RPA) that operates on rule-based tasks, APA is dynamic, handling decision-making and adapting to evolving circumstances by sensing, evaluating, and responding to its operating environment. APA pairs AI's high-level cognitive abilities with automation capabilities, enabling systems to execute tasks involving planning, reasoning, and adaptation. For example, in an APA environment, an LLM-based agent could autonomously generate a workflow after receiving a set of instructions, making use of other specialized agents or tools for actions like data analysis or customer interaction.
Features checklist for automation software tools.
The proliferation of automation software tools has led to a dizzying array of specialized features that aim to distinguish one provider from another. However, certain core capabilities remain essential for achieving automation success. Key features such as task automation and scheduling, along with integrations and security, are critical and consistent across software solutions, including low-code platforms and function-specific tools like automated email marketing, lead generation, and social media management.
Task automation
Aimed at automating individual tasks within the business processes, this feature minimizes manual effort and streamlines operations.
Workflow automation
Workflow automation is the ability to automate the sequential flow of tasks within a particular process or project, rather than across systems. Workflow automation features enable users to set up routines that execute series’ of tasks automatically.
Process automation
Process automation involves automating a series of tasks or steps in a specific business process, typically across multiple departments, data sets, systems, and apps. Process automation features enable bridging disparate systems as well as orchestration tools to coordinate process steps.
Scheduling
Automation scheduling is an essential feature to plan and coordinate process execution. Even for individual tasks, scheduling operations is key to getting the right work done at the right time to enable effective workflow and output.
Integrations
Connecting with and integrating across diverse systems, data sources, and applications is a foundational feature set of automation software.
Customizable workflows
To meet specific business needs, automation software should offer customizable workflows. This allows businesses to create unique workflows aligning with their respective processes.
Reporting and analytics
Keeping track of automation performance ensures automations deliver the intended results and any issues can be addressed before a critical failure. Automated reporting capabilities of automation software assist in continuous performance monitoring and data-driven decision making.
Real-time data
Ensuring that all data is current and accurate is only possible with real-time data syncing features. This helps maintain data integrity and consistency across different systems.
Support
Automation software is usually easy to use, however technical assistance, training, customer success, documentation, and community engagement, remain standard—and helpful—support offerings across providers.
Scalability
Scalability is a core feature of automation software infrastructure and design. Scalable software can accommodate volume fluctuations and growth, able to adjust to and support workload variations. Highly scalable automation software enables right-sized technology investments that can grow with business needs.
Collaboration
Tools for collaboration are a core feature of automation software that will be used for more than individual task automation. Stakeholders involved in defining processes and designing automated workflows must have easy access to collaborate, review, and approve within the tool.
Mobile access
Accessing work applications from mobile phones is standard practice today. Automation software is no exception; mobile access is valuable in particular to enable oversight and ensure automated workflows progress smoothly from anywhere.
Data privacy and security
Automations interact with business systems and data that must remain safe and uncompromised, making security and data privacy features fundamental to any automation software solution.
Function-specific features
For automation software solutions that address a particular industry or functional area, such as sales and marketing or finance and accounting, must-have capabilities will include function-specific capabilities like segmentation tools for email marketing automation software or lead management tools for marketing automation software.
How to evaluate enterprise automation software.
For enterprises, a comprehensive automation platform is essential for driving digital transformation. When evaluating automation software, focus on the range of capabilities and solutions offered by a vendor, the ease of scalability and interoperability, and how their technology and commitment to innovation can support a future-proof digital transformation journey. A strong enterprise automation solution will enable seamless integration of automation and AI technologies, maximizing existing investments while minimizing the complexity and costs associated with redundant technologies.
Ease of use
Enable your workforce to engage with automation by choosing a unified automation solution with apps and tools they can easily use. Leverage the power of generative AI by selecting software with conversational automation assistants that enable business users to find and run automations in natural language. These automation co-pilots bring automation to employees by embedding it within work applications and enabling users to call AI agents and orchestrate workflows across systems and teams. Look for solutions that offer a complete developer toolkit while also empowering business users (and accelerating developers) with an intuitive, drag-and-drop automation creation experience.
AI-assisted development
Accelerate automation development with AI to seamlessly identify processes and transform documentation into functional automations at scale. Generative AI is transforming the process of automating, enabling professional and citizen developers to use natural language prompts to create end-to-end automations. Look for AI-assisted automation development capabilities that accelerate the automation lifecycle and enable developers to safely infuse generative AI within workflows.
Process orchestration
Business processes don’t operate in a vacuum. Workflows and their outputs must connect and be synchronized with the work of every team and department across enterprise operations. To align and coordinate process automations, ensure any considered solution offers robust process orchestration tools, including a comprehensive suite of capabilities such as intuitive workflow design, plug-and-play integrations and APIs, robust task automation and scheduling, and real-time monitoring and analytics.
Data management and integration flexibility
Seek out core integration capabilities that enable seamless connection to business applications via pre-built packages, sophisticated workflow automation through iPaaS integrations, and support for developers of all skill levels to drag and drop APIs into any process.
Integrations and APIs
Embed automation within existing technology and team workflows by selecting a platform with pre-built connectors for core systems and work apps. Insist on core integration capabilities to connect business applications via pre-built packages, enable workflow automation through iPaaS integrations, and support developers of all skill levels to drag and drop APIs into any process.
Cloud-native architecture
Scale automation smoothly and securely by selecting automation technology that has a cloud-native microservices architecture and flexible deployment model. Choosing a cloud-native platform ensures high availability and disaster recovery (HA/DR) are standard features.
Agentic automation
Future-proof your automation strategy by choosing a solution that supports agentic automation. AI agents power end-to-end automation of cognitive workflows. Look for platforms that facilitate no-code development of AI agents and enable agents to integrate with existing enterprise architecture, AI models, applications, and systems. Supporting features must include robust security and governance to ensure responsible AI deployment.
Trust and security
Secure your business data and process automations by looking for enterprise-class reliability with high availability and defense-in-depth security standards and certifications, including SOC 1 Type 2, SOC 2 Type 2, ISO 27001, HITRUST, and ISO 22301. Comprehensive solutions will comply with industry-specific regulations, adhere to GDPR and data privacy principles, including the encryption of sensitive information, and provide essentials-only cloud storage.
Training and support ecosystem
Successful automation software implementation and performance will depend on a provider that offers effective training and a global support ecosystem. Look for robust support resources and guidance to establish a foundation for automation success by learning from similar deployments, strategies, and operating models to apply the best-fit approach to your organization.
Use cases for automation software.
Finance and accounting
- Invoice processing: Automate the approval and payment process for invoices to reduce manual errors and speed up transactions.
- Expense management: Streamline the submission, approval, and reimbursement of employee expenses.
- Financial reporting: Automate consolidation and generation of financial reports to ensure accuracy and compliance.
Human resources
- Recruitment and onboarding: Automate job postings, candidate screening, interview scheduling, and onboarding processes.
- Employee data management: Maintain and update employee records, benefits administration, and payroll processing.
- Performance management: Automate performance review cycles, goal setting, and feedback collection.
Marketing
- Campaign management: Automate the planning, execution, and analysis of marketing campaigns across multiple channels.
- Lead nurturing: Streamline lead scoring, nurturing, and conversion processes through automated email workflows.
- Social media management: Schedule posts, monitor engagement, and analyze social media metrics.
Sales
- Customer relationship management (CRM): Automate lead tracking, customer follow-ups, and sales pipeline management.
- Quote and proposal generation: Streamline the creation and approval of quotes and proposals for prospective customers.
- Order processing: Automate order entry, confirmation, and fulfillment processes to enhance customer experience.
IT and support
- Incident management: Automate ticketing systems for managing IT incidents and service requests.
- System monitoring: Use automation to monitor system performance, detect anomalies, and trigger corrective actions.
- Software deployment: Streamline deployment, updates, and patch management of software applications.
Manufacturing
- Production scheduling: Automate scheduling and coordination of production activities to optimize resource use.
- Quality control: Implement automated quality checks and inspections to ensure product standards are met.
- Inventory management: Streamline the tracking and management of inventory levels and reordering processes.
Healthcare
- Patient record management: Automate the maintenance and updating of electronic health records (EHRs) for better patient care.
- Appointment scheduling: Streamline scheduling and reminders for patient appointments.
- Billing and claims processing: Automate the submission and processing of insurance claims and patient billing.
Retail
- Online order fulfillment: Automate picking, packing, and shipping processes for online orders to improve delivery speed.
- Customer service: Implement chatbots and automated response systems to handle customer inquiries and support.
- Inventory management: Use AI and automation to predict inventory needs and trigger reordering processes.
Logistics and supply chain
- Shipment tracking: Automate shipment tracking and delivery status notifications.
- Supplier management: Streamline communication/coordination with suppliers to drive on-time delivery.
- Warehouse management: Automate managing warehouse operations, including inventory tracking and order fulfillment.
Financial services
- Fraud detection: Automate monitoring transactions for potential fraud and triggering alerts for suspicious activities.
- Regulatory compliance: Streamline compliance reporting and documentation processes to strengthen adherence to industry regulations.
Telecommunications
- Network management: Automate monitoring and maintenance of telecom networks to ensure uptime and performance.
- Customer onboarding: Streamline activation and setup processes for new customers.
Education
- Student enrollment: Automate application and enrollment processes for new and returning students.
- Learning management: Streamline administration of online courses, including content delivery and assessment.
The evolution of automation software.
Automation software isn't new, but it has advanced at lightning speed over the last decade. With the infusion of artificial intelligence (AI), the horizons of automation are expanding, redefining the possibilities of automating business operations.
Early days: OCR and basic automation
Automation tools have come a long way in a short time. Technologies like optical character recognition (OCR) made it possible to automate mundane document and data processing tasks and transform paper documents into digital format, laying the groundwork for digital operations. However, the scope of automation was limited to basic task automation of repetitive, error-prone, and time-consuming data-related tasks.
Tool proliferation: RPA, RDA, BPA, IDP
The introduction of robotic process automation (RPA) marked the beginning of rapid automation software adoption and corresponding proliferation of tools and technologies, including robotic desktop automation (RDA), business process automation (BPA), and intelligent document processing (IDP). The tagline "there's a bot for that" aptly captures this phase of the evolution of automation software as companies began to apply separate automation tools to disconnected processes across different departments.
Better together: Intelligent Automation
As automation technologies matured, the integration of AI marked the beginning of a new era. Intelligent Automation, combining AI and machine learning with traditional automation tools, enabled coordinated, strategic enterprise automation efforts. Orchestration and seamless integrations allowed technologies, systems, and data to work in harmony, powering cohesive end-to-end process automation.
The future: Generative AI and AI agents
The future of automation software is deeply linked with advancements in AI. Generative AI and the emergence of AI agents represent a step change in the automation software landscape. AI agents, combining generative AI with automated action, can execute and manage cognitive tasks, making informed decisions based on real-time data and inputs, redefining the boundaries of what automation software can achieve.
How to get started with automation software.
Welcome to the journey of finding and implementing automation software. This journey is not only about applying new software; it’s about creating both operational and cultural change to drive efficiency, productivity, and, ultimately, transformation.
Evaluate
Before you can automate, you need to select the right software that aligns with your business objectives. One approach to building an understanding of your software needs is to identify repetitive time-consuming tasks within your organization and associated data and system requirements. With so many automation software options available, each with strengths and specialties, choosing a provider will involve research and strategically evaluating both immediate business needs and longer-term goals.
Learn
After selecting software, ensure your automation team gains a comprehensive understanding of its functionality. Investing time in mastering the software's capabilities will yield long-term benefits by enabling your organization to use it effectively. Utilize training and tutorials, webinars, and customer support to expedite the learning process.
Automate
Next, consider starting small and gradually scaling up. Automation is a journey rather than a destination. Many organizations begin by automating straightforward tasks and then advance to more complex processes. This approach has the advantage of building your understanding of automation within your business context and allowing you to incrementally learn how to apply your selected software to more complex use cases.
Optimize
After getting started, ongoing review and optimization are the keys to automation success. Automation is not a set-it-and-forget-it effort; ongoing performance monitoring and periodic evaluations of automated tasks and processes will provide insights into their effectiveness and highlight areas for improvement. Make necessary adjustments and continue to refine your processes for optimal results.
Get started with the complete AI + Automation Enterprise System.
Get support for the entire automation journey, including workforce management, systems integration, security, and scalability, with the complete AI + Automation Enterprise System. Achieve automation success with resilient AI-powered automations, rapid deployment, and effective governance.
Frequently asked questions.
What are some examples of automation in business operations?
Automation can be found across nearly every business function and industry, revolutionizing business operations with its transformative impact on efficiency and productivity.
- In manufacturing and logistics, automated inventory management systems track stock levels, reorder when necessary, and optimize storage, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Examples of automation in finance include continuous transaction monitoring for fraud detection using machine learning models to flag activities for investigation.
- Human resources operations use automation to enhance recruiting with automated resume screening and interview scheduling.
- Sales and marketing use automation for lead scoring, nurturing, and personalized content delivery to drive engagement and conversions.
- IT operations apply automation in network monitoring systems that detect and resolve issues and in automated backups to ensure data integrity and security.
How accurate is automation software?
Automation software is designed to execute tasks and processes with near-perfect accuracy and consistency. However, the accuracy of automation software depends on factors such as the quality of data inputs, the complexity of a task/process, and the models employed to complete the work. By continuously learning from data patterns and feedback, AI-powered automation software can refine execution to improve accuracy over time. As well, automation tools often include validation mechanisms and error-checking algorithms to ensure the reliability of results. While no system is entirely error-proof, automation software sets a high bar for accuracy, efficiency, and overall performance of business operations.
Does automation software use machine learning?
Automation software doesn't require machine learning to perform basic functions. However, adding machine learning (ML) and other AI tools expands the capabilities of automation software by an order of magnitude. Machine learning empowers automation software to adapt to new data patterns, learn from past actions, and make intelligent decisions without explicit programming. By incorporating ML algorithms, automation software can enhance its predictive capabilities, optimize workflows, and customize processes.
Can automation software provide real-time insights?
Yes, automation software can provide real-time insights into business and process performance. Automation software collects and logs details on every aspect of the processes, data, and systems it connects with. By continuously monitoring and analyzing this data in real time, automation software can generate valuable insights into workflow efficiency, resource utilization, and business performance. These insights help organizations make informed decisions, identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and quickly respond to change.
How does automation software integrate with existing business systems?
Automation software integrates with existing business systems by leveraging robust APIs and connectors to establish communication between different platforms and tools. Integrations ensure seamless automation operation and data flow. Integration methods include:
- API integration: Many automation tools use Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to connect with business systems. APIs enable sending and receiving data, triggering actions in other software applications. APIs facilitate real-time data exchange and ensure that automated processes can interact with business systems.
- Pre-built connectors: Some automation platforms offer pre-built connectors for popular business applications like ERP, CRM, and HRM systems. These connectors simplify the integration process by providing ready-made solutions for common integrations.
- File-based integration: For systems that do not support APIs, file-based integration enables exporting data from one system in a file format (such as CSV or XML) and then importing it into another system. Automation software can manage this process, ensuring data transfer is accurate and on schedule.
- Database integration: Automation tools can connect directly to databases to read and write data. This is useful for integrating systems that store their data in relational databases, allowing the automation software to perform operations like data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL).
- Robotic process automation (RPA): RPA uses software robots to mimic human interactions with application UI. This approach is particularly useful in the case of legacy systems that do not support integrations.
- Custom scripting/programming: For more complex or unique integration needs, custom scripts or programs can be developed. Scripts can be tailored to the specific requirements of business systems and processes.
What types of tasks should be automated to improve business processes?
Automating nearly any type of task can help improve business processes by delivering higher efficiency, consistency, and speed. Organizations can strategically prioritize automation to improve business processes, starting with repetitive, time-consuming manual tasks such as data entry, report generation, and routine administrative functions where high accuracy and speed are essential. Other prime candidates for automation include tasks that take human employees away from high-value activities, such as building customer relationships. To this end, improving customer service processes can be supported by automating tasks such as responding to frequently asked questions, managing inquiries, and routing requests. Business processes involving data analysis and interpretation can also benefit from the real-time insights automation can deliver, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making.







