What is business automation?
Business automation is the application of software solutions to execute recurring tasks or processes in an organization.
Also known as business process automation (BPA), business automation is a core tactic supporting the strategic goals of business process management. It involves using technology to streamline and automate business processes in order to increase efficiency and performance, reduce costs, and digitally transform operations. An automated business process delegates digital work tasks—multi-step, multi-system, and cross-functional—to automation software to execute and manage.
Benefits of business automation.
Increase speed, effectiveness, and productivity across enterprise operations with business automation to execute and optimize tasks and processes.
Save
time and increase productivity and efficiency by automating time-consuming processes to accelerate business outcomes and free employees for higher-value work.
Reduce
costs with business automation by eliminating process delays, variations, and incidents of human error.
Improve
accuracy and consistency by establishing optimal workflows and putting them on repeat.
Scale
with business growth by seamlessly handling increases in volume without errors or capacity constraints.
Delight
customers by delivering faster response times and freeing agents to provide more personalized service.
Types of business automation.
There are many overlapping terms for approaches to automating business processes. The primary difference between automation strategies or technologies lies in the scope of their capabilities to automate across diverse tasks, processes, and workflows, as well as integrate with the data, systems, and people involved.
BPA and workflow automation broadly represent types of software tools to automate business processes rather than individual or isolated tasks. It is important to note that business process automation is not the same as business process management (BPM), an operational discipline for managing organization-wide processes. Another type of business automation is robotic process automation (RPA). RPA is a specific software technology that underpins many business automation platforms, enabling the capture, automation, execution, and management of repetitive, rule-based tasks.
However, business processes are rarely linear or static; most enterprise workflows require decision-making and adaptability to dynamic, unplanned scenarios. To address this reality, the business automation industry has evolved to integrate powerful artificial intelligence (AI) technologies throughout the automation lifecycle, supporting the flexibility and unpredictability of actual business operations. Cognitive automation and intelligent automation, or AI-powered automation, represent the current advancement of business automation.
Business process automation (BPA)
General term for using software to automate business processes, including all-purpose automation platforms and function-specific applications like CRM.
Robotic process automation (RPA)
RPA software technology powers the capture, automation, execution, and management of repetitive, rule-based tasks.
Intelligent document processing (IDP)
Applied AI technology to automate the processing of unstructured data from documents such as invoices, forms, and contracts, supporting end-to-end process automation.
Intelligent Automation
Also known as AI-powered automation, combines cognitive technologies like NLP and machine learning with RPA to automate complex processes.
Cognitive automation
AI technologies that mimic human thought processes and decision-making in automating complex tasks and processes.
Workflow automation
The use of software tools to automate work tasks and end-to-end processes. Another term for business process automation.
What to look for in a business automation solution.
Business automation has become an essential tool for organizations of all sizes and across industries, and solutions for business automation have proliferated, offering an ever-growing range of tools and technologies to help streamline operations and achieve digital transformation goals. Overall, when selecting a business automation vendor, it is important to prioritize security and scalability combined with integrated cognitive technologies, such as generative AI, that are rapidly redefining the speed and scope of business automation capabilities.
Ease of use
Ease of use may be the number one criterion in evaluating business automation solutions. Unlike other software technologies, ease of use for business automation means much more than having an intuitive interface. Enabling automation to reach every corner of operations means automation tools must be accessible for business users without advanced technical skills or training in AI modeling while also supporting and speeding up the work of expert automation developers. At the same time, enterprise automation still requires mapping complex workflows and logic as well as integrating across enterprise systems and apps. Future-proof business automation solutions already bridge these divides by harnessing generative AI to fuel process discovery and automation development following natural language prompts, accelerating and simplifying the idea-to-automation journey.
Integrations, connectivity, and scale
Choose an automation solution to not only meet current business requirements but also to be scalable and flexible enough to accommodate future business needs. The solution should flawlessly connect to any business application you use, with native connectors and pre-built packages to drag and drop into automation workflows. APIs can also be available as no-code automation building blocks. Support scale by opting for an automation solution that runs fully in the cloud for execution speed, flexibility, and real-time data interactions.
Automation for citizen (non-technical) developers
Along with in-depth automation training and expert-led guidance, look for tools that empower non-technical employees, known as citizen developers, to safely and effectively contribute to an organization's business automation efforts. Generative AI-assisted automation leverages natural language prompts to create and refine process automations, regardless of coding expertise. Utilizing citizen-developed automation requires maintaining coding standards and verifying code quality. It automatically identifies errors, bottlenecks, and best practice violations. Built-in code quality analysis capabilities can automatically identify errors, bottlenecks, and best practice violations. Effective solutions offer governance and guardrails to ensure secure, high-quality automations with required reviews before going live.
Enterprise-grade security and compliance
Because automating business processes involves core operating systems and potentially sensitive data, security and compliance are critical aspects to evaluate before choosing a business automation solution. Look for strong data privacy practices and secure data encryption (i.e., AES-256 encryption, FIPS-140 certified). Consider authentication/authorization. How is access managed and credentials stored? Look for identity and access management (IAM). Make a checklist of industry compliance standards like GDPR, ISO 22301, ISO 27001, SOC 1 Type 2, SOC 2 Type 2, and HITRUST. Ensure vendors have performed water-tight risk assessments, vulnerability assessments, and compliance audits to support and maintain your security posture.
Deployment flexibility
Leading business automation providers support multiple deployment options even with fully cloud-native automation platforms. Platforms should be ready to use right out of the box and not require any special infrastructure, with options to deploy either in the cloud—and seamlessly leverage cloud providers like AWS and GCP—or remain on premises, hosting on your own infrastructure. Look for global high availability and disaster recovery (HA/DR), and highly scalable, multi-tenant architecture that includes auto-scaling capabilities to optimize performance and minimize bottlenecks.
Intelligent document processing (IDP)
Selecting the right business automation solution includes evaluating document automation capabilities. Not all business automation platforms offer embedded intelligent document processing (IDP); buyers should look for solutions that natively harness AI-powered document processing for accurate data extraction that integrates seamlessly with automated workflows to drive end-to-end process execution. Foundational capabilities include excellent document classification and separation to accurately identify relevant pages within multi-page documents, but advanced data extraction and validation capabilities are critical for precise and reliable results. Advanced offerings will be able to improve document quality through techniques like noise reduction and de-skewing. Flexibility and customization features help for tailoring document automation to specific business needs, including support for multiple languages. Prioritize solutions with strong data protection and support for regulatory compliance. Pre-built document models can significantly reduce configuration time, and the solution should be versatile enough to cater to your industry-specific requirements.
Automation center of excellence (CoE) support
Your automation center of excellence (CoE) can be the determinant of automation program momentum and success. When selecting a solution, prioritize those that offer training and expert guidance along with purpose-built CoE management tools. CoE tools should deliver program-wide visibility and control, including built-in KPI and ROI tracking to measure time saved, cost efficiency, operational agility, and financial impact. Seek tools that can help accelerate pipeline by facilitating the submission of automation ideas as well as identifying and consolidating automation opportunities through integrations with work applications employees use, such as JIRA or ServiceNow.
Business automation use case examples in different industries.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Automation can streamline customer service operations by automating routine queries, accelerating credit card processing, and speeding up the KYC process, ensuring quick responses and improved customer satisfaction.
- Improved Compliance and Fraud Detection: Ensure regulatory adherence and enhance security through automation of compliance processes, KYC protocols, and fraud detection systems, swiftly identifying and addressing irregularities.
- Optimized Financial Operations: Boost efficiency and accuracy in financial processes by automating accounts payable, loan fulfillment, and general ledger reporting, reducing manual errors, and expediting essential banking functions.
- Cost Reduction and Efficiency Improvement: Business automation can improve revenue cycle management, expedite patient care by automating processes such as prior authorization, and drive the accurate, timely transfer of information through automated document data extraction.
- Enhancing Patient Experience: Automate patient-centric processes, such as pre-admission, registration, and scheduling, to simplify check-ins and reduce wait times. Automate point-of-sale collections and telemedicine setup to deliver better patient experiences even in remote care environments.
- Risk Management and Data Insights: Apply automation for audits, preventive care alerts, and fraud detection to help mitigate risks. Automation also helps in the integration and interoperability of systems and can improve predictive analytics for better decision making by providing real-time operational dashboards.
- Operational Efficiency and Compliance: Improve demand planning, sales forecasting, and supply chain management. Optimize financial management tasks such as account payables and inventory management to reduce costs and increase compliance.
- Customer Experience: Automate case triage, escalation, and real-time data capture to deliver seamless, personalized interactions.
- Innovation and Data Insights: Drive innovation by automating product development processes like BOM management and product testing simulations. Automate reporting and analytics to streamline the collection and interpretation of data for informed decision making.
- Adverse events and Complaints: Apply business automation to accelerate the intake and triage of complaints, pull information from multiple sources, systems, and types of documents, complete forms, and send follow-up communications.
- Supply chain: Automate procurement, stockpiling, and inventory adjustment processes, onboard new suppliers and coordinate supply chain program management, and secure and adjust logistics and transportation options.
- Clinical studies: Use Intelligent Automation to create regulatory documentation and audit filings, prepare regulatory forms for preclinical and clinical development, and complete clinical database and research reports.
The evolution of business automation.
The productivity imperative, paired with the ever-growing demand for faster and more accurate processes, is propelling innovation in business automation, with recent advancements harnessing generative AI.
Enterprise systems
Business automation began in earnest with the arrival of enterprise systems— such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software—to align and manage global business operations by integrating various functions like finance, HR, and supply chain management into a single unified system. Enterprise systems delivered broad business benefits, including improved data accuracy, reduced operational silos, and more streamlined workflows. Through the use of integrated enterprise systems, organizations saw the potential for deeper process transformation to further streamline operations and create a step change in efficiency.
Process improvement
Business process management (BPM) emerged to address the need for process transformation. BPM tools provided organizations with capabilities to model and optimize processes beyond the scope of enterprise systems like ERP. BPM tools offered a more granular approach to process improvement, focusing on efficiency and agility. But even as BPM evolved to encompass more advanced capabilities like process monitoring and analytics, automating processes remained a slow, IT-heavy endeavor. The need to increase productivity enterprise-wide and much faster demanded a solution. This demand made way for the development of accessible business automation technology.
Accessible automation
The critical leap to accessible automation tools arrived in the 2010s with the development of robotic process automation (RPA). RPA introduced the concept of intuitive automation software to quickly and easily configure programs to mimic human digital activities and perform repetitive, rule-based tasks. This business automation technology allowed for vast improvements in operational efficiency and immediate cost savings by eliminating process execution errors. In addition, RPA's ability to work across multiple enterprise systems without the need for integrations meant it could deliver ROI in a fraction of the time of legacy automation projects.
AI + automation
Business automation has reached a new frontier with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, including generative AI. Intelligent Automation leverages AI to not only execute cognitive tasks but also to process complex documents and data, learn and improve from experience, and enable exponentially faster automation development. This evolution is rapidly closing the productivity gap, enabling enterprises to automate and safely harness generative AI to speed digital transformation and ultimately gain a competitive edge in a dynamic global market.
How to get started on your business automation journey.
Begin your business automation journey by planning strategic first automations, establishing your center of excellence (CoE), and thinking ahead to scaling up with security and flexibility.
Getting started
Starting your business automation journey
While there is no wrong way to begin, it's a misconception that unimportant, simple processes should be automated first; on the contrary, it's key to automate high-value, even complex, processes first to build a clear understanding of what automation will involve for the organization as well as to realize tangible ROI on initial automation projects, which will drive program expansion. Consider processes that require speed and consistency, where errors come with high costs. Readying the organization and pinpointing processes to automate involves internal and external discussions, exploring industry best practices and tools, and envisioning the overall transition to automated digital operations. Involving HR from the start can help ensure a realistic approach and openly address any concerns.
Readiness
Gearing up to automate with the right tools and technologies
As a core strategic tool to drive productivity and competitiveness, evaluate business automation vendors against both immediate and long-term criteria such as security, scalability, integrations, and innovation track record. At the same time, build internal readiness by establishing an automation center of excellence (CoE) with a clear governance structure and taking the opportunity to learn from business automation implementations in your industry. Use these learnings to define goals for your automation initiatives and set benchmarks and success criteria.
Automation
Developing and implementing business automation
Build out the first process automations by working step by step through each phase, from process discovery and mapping to workflow design to testing and deployment. The aim of these initial automations is to thoroughly flesh out your enterprise's unique environment in order to validate assumptions and implementation models, as well as measure the impact of automation against your success metrics and change management plans. Looking ahead, the automation phase will become the heartbeat of your business automation program, with continuous monitoring and improvement to fine-tune processes for optimal results.
Scale
Growing your automation program and managing change
Automation really is a journey, not a destination. Plan to continuously improve, expand, evaluate, and experiment across automation initiatives to ensure the long-term success of your business automation strategy. Nurture workforce adoption of automation by empowering employees to participate, whether by submitting automation ideas or building automations on their own as citizen developers. Keep communication channels open by sharing and promoting internal automation success stories, as well as listening to employee needs and feedback.
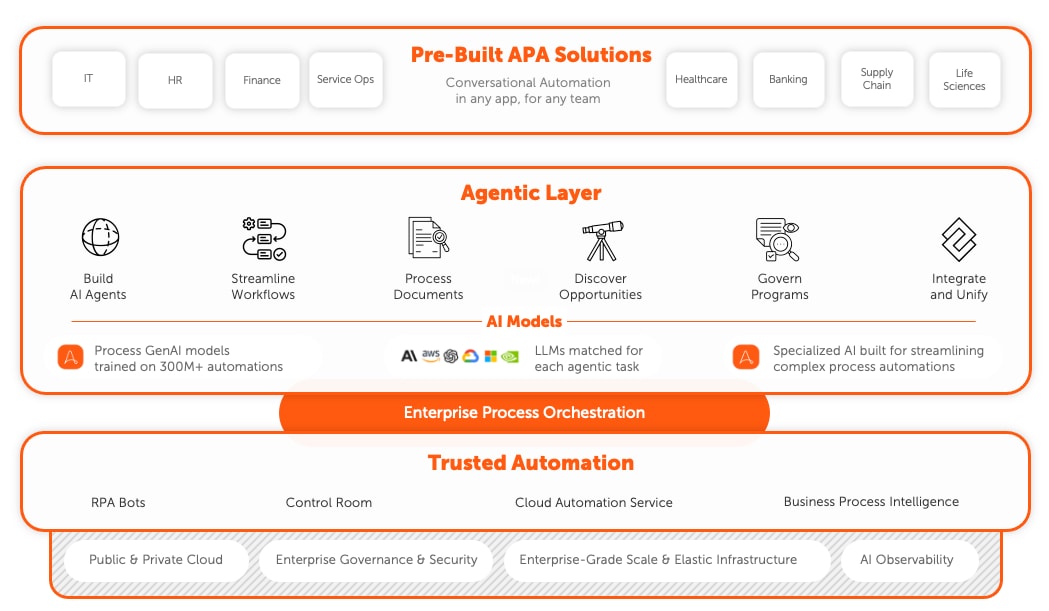
How a complete AI-powered automation platform supports business automation.
Achieve successful business automation with quick, flexible automation development and integration by leveraging the Agentic Process Automation System. Get support for the entire automation journey, including workforce management, systems integration, security, and scalability, to enjoy resilient automations, rapid deployment, and effective governance.