The benefits of business process management.
By refining operations across the organization, BPM delivers tangible benefits that can significantly transform operational efficiency and productivity.
Increase productivity
Removing bottlenecks and refining processes drives better performance and seamless work.
Reduce costs
Enjoy cost savings by driving efficiencies organization-wide.
Greater visibility and control
Gain insights and better control over process performance by tracing items through their workflow.
Improve efficiency
By streamlining and optimizing processes, BPM reduces costs and drives higher-quality products and services.
Drive digital transformation
In tandem with Intelligent Automation, BPM strategies power enterprise-wide business process transformation.
How does BPM work?
Business process management (BPM) strategies work by systematically organizing, analyzing, and refining business processes to align them with overarching business goals. Supported by advanced process modeling techniques, BPM helps with the visualization and comprehension of existing processes to better monitor, measure, and automate these processes.
The methodology of BPM involves key stakeholders to design processes attuned to the multifaceted needs of the business. Through a cycle of steps, including process design, modeling, execution, monitoring, and optimization, BPM can make a powerful impact on productivity, efficiency, and agility by cutting costs, boosting the quality of products or services, and improving response times to market changes and technology advancements. Ultimately, BPM works by becoming a cornerstone of organizational culture that strives for continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Business process vision
BPM is vision-driven, starting with documenting clear process goals and involving stakeholders to build a complete picture of a process’s purpose.
Mapping and monitoring
To fully comprehend processes, BPM utilizes process modeling techniques and evaluates processes through continuous monitoring and performance measurement.
Culture of optimization
To propel automation and the optimization of processes, BPM must be supported by technologies and an organizational culture that prioritizes continuous improvement.
Apply BPM to use cases in any industry.
BPM has proven its versatility and effectiveness across industries to optimize processes and catalyze growth.
Financial Services
Streamline complex processes that strengthen security and compliance to mitigate risk and boost balance sheets.
Manufacturing
Eliminate waste, reduce costs, and speed up time-to-market by boosting efficiency on the factory floor and back-office.
Life sciences
Speed up workflows, remove bottlenecks, and eliminate silos to accelerate pharmacovigilance and complaint handling.
Healthcare
Streamline workflows and systems to offer exceptional patient experience, robust security, and guaranteed compliance.
The evolution of BPM.
Business process management has been transforming the enterprise for years—here’s a look at its past, present, and future.
Getting started
Business process management has been around as long as business processes. A foundational concept, BPM was first introduced in the 1990s and has evolved significantly since then. In its early days, it primarily focused on automating processes to reduce costs and required heavy IT investment.
Getting things done
The rise of low-code automation tools such as robotic process automation (RPA) opened the floodgates of process improvement. Organizations could see the return on investment from BPM efforts much sooner, quickly cementing the synergistic relationship between BPM and automation technologies.
Getting smart
Intelligent Automation has supercharged BPM approaches by facilitating rapid process discovery, automation, and optimization. In particular, generative AI embedded within Intelligent Automation solutions makes it possible to execute complex BPM methodologies and reshape what productivity looks like.
Making change
The future impact of BPM is closely related to the rapid evolution of Intelligent Automation technology. Advancements in AI —particularly with AI agents— and other emerging technologies will continue to push the boundaries of process optimization and innovation, reshaping BPM as we know it.
Chart your journey to transform every business process.
Meet the demands of digital transformation with intelligent solutions for BPM and automation that work alongside each other.
Plan
Define your transformation strategy and vision Business processes aren’t just about getting things done; they embody competitive advantages and determine profitability. That’s why the race is on to innovate, accelerate, and simplify business processes toward digital transformation. Begin your process transformation journey by choosing the methodologies that will guide your digital transformation vision.
Evaluate
Choose the right technologies Digital transformation tools are abundant. Look for a partner that is dedicated to long-term innovation. Many vendors excel in certain areas of business process automation. Make sure your BPM partner integrates with Intelligent Automation to guarantee better business outcomes.
Engage
Automate to realize BPM goals Once a process is redesigned, automation technologies are applied to achieve optimal efficiencies in the execution of the new process workflow. Automation doesn’t need BPM to make a major impact on process performance. But BPM needs automation to bring transformed processes to life.
Expand
Unlock the benefits of end-to-end process management BPM is essential for any digital transformation journey, but it is greatly enhanced by Intelligent Automation. This combination boosts productivity at every step, helping you discover new opportunities for process improvement. BPM and Intelligent Automation together represent a direct route to end-to-end enterprise efficiency.
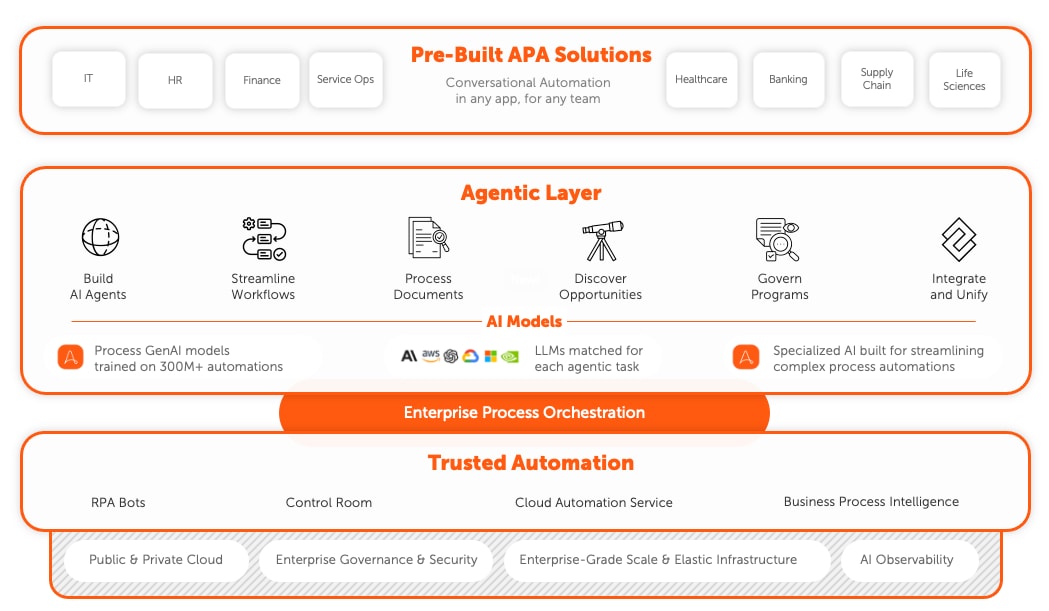
Accelerate digital transformation with Intelligent Automation.
The Agentic Process Automation System supports the many facets of your digital transformation journey, including your workforce, integration with existing systems, security, and scalability.
Frequently asked questions.
Why are business process management systems important?
BPM gives organizations a set of solutions and methodologies to foster the continuous improvement of enterprise efficiency. The goal of BPM is to redesign existing processes in order to streamline business operations and drive digital transformation. It’s an essential tool to deliver business value and a competitive edge.
What are the steps in the BPM lifecycle?
BPM initiatives follow five steps. 1. Design: Work out the ideal state of a process and how to achieve it. 2. Model: Test how workflows play out in different scenarios. 3. Implement: Set up BPM tools like RPA and begin automating. 4. Monitor: Analyze the results and identify areas to optimize. 5. Iterate: Act on the data for continuous improvement.
What are the different types of business process management?
There are many aspects to a BPM suite. Process discovery identifies areas for improvement. Process orchestration connects your people, processes, and systems. Process modeling and workflow management optimize the steps in any given workflow. RPA learns new processes in real time. Process intelligence metrics monitor data and offer insights.
How does business process management compare to robotic process automation (RPA)?
Although distinct solutions, BPM and RPA work together hand-in-glove. BPM is a set of overlapping solutions and methodologies to optimize process efficiency. RPA is one unique solution that uses self-learning automation software to achieve very similar business goals to BPM. The best business strategy is to use both to complement each other.
What features should you look for in business process management software?
The features to look out for in business process management tools include: 1. Easy-to-use, ideally low-code or no-code interfaces with drag-and-drop functionality and visual dashboards, 2. Seamless integration with apps and APIs, including ERP, CRM, and legacy systems, 3. Artificial intelligence capabilities to futureproof your BPM investment.
What types of processes can a business process management initiative improve?
BPM technologies provide business value by removing repetitive tasks and bottlenecks caused by messy workflows. If you can think of an existing process or ad hoc set of activities, they can be improved, including approvals, onboarding, and document-centric work. They can also help CIOs, project managers, and knowledge workers alike with their KPIs.




