The benefits of SAP automation.
SAP automation helps organizations maximize the speed and effectiveness of enterprise resource planning efforts while decreasing the amount of human error involved in executing SAP processes.
Speed
data access SAP automation delivers faster access to data to drive customer service effectiveness, ensure accurate reporting, and inform business decisions.
Reduce
errors and costs by automating data entry, reconciliation, and reporting processes across SAP systems.
Strengthen
governance and compliance. Automating SAP business processes reinforces adherence to data governance and regulatory compliance standards.
Boost
productivity by automating both basic tasks and complex workflows using the SAP ecosystem, freeing SAP end users to concentrate on higher-value activities.
Improve
the efficiency of SAP process execution and enable further process improvements through customizations and optimization.
How does SAP automation work?
SAP automation works by applying Intelligent Automation technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI) to automate processes within and between SAP and other business applications.
The first step in SAP automation is analyzing existing processes to identify areas that can be automated and zeroing in on the highest-value automation opportunities. Intelligent Automation platforms can accelerate this process with automated process discovery tools that harness generative AI to assist in developing functional automations from process documentation.
Discover SAP processes
Identify processes with high potential for automation utilizing intelligent process mining tools.
Build automations with AI
Develop SAP automations from process documentation using AI-assisted low-code automation creation workflows.
Test and deploy
Validate and deploy automations quickly using low-code automation tools and orchestrate automations across SAP and other business systems.
Monitor and improve
Track automations with real-time analytics and intelligent insights, optimizing processes for maximum efficiency.
What to look for in an SAP automation solution.
Automating SAP processes requires the full spectrum of Intelligent Automation tools, from process discovery to real-time visibility into process performance—and everything in between. Enabling non-technical SAP process stakeholders to automate (and accelerating the automation lifecycle for developers) calls for tools that allow users to visually design and adapt process flows, manage decision logic, and automate and orchestrate tasks and workflows both within and outside of SAP. Top solutions incorporate built-in AI capabilities for intelligent document processing and generative AI that do not require specialized data scientist support. Key capabilities to look for include intuitive workflow management, robotic process automation (RPA), and embedded artificial intelligence (AI) and generative AI.
Low-code automation with AI
Generative AI is transforming the process of automating, enabling professional and citizen developers to use natural language prompts to create end-to-end automations. Look for solutions that offer a complete developer toolkit while also empowering business users (and accelerating developers) with an intuitive, drag-and-drop automation creation experience.
Unified development experience
Robust Intelligent Automation tools will include developer-oriented tools and documentation that make it simple for developers to build dependable, resilient, easy-to-maintain SAP process automations. Look for AI-assisted automation development capabilities that accelerate the automation lifecycle and enable developers to safely infuse generative AI within workflows.
SAP partnership
Automating with an SAP partner provides opportunities to boost enterprise automation efforts, increase efficiency, reduce costs, and maximize the value of technology investments. Established platform integrations with SAP applications enhance workflows and governance, offer pre-built automation and swift integration capabilities, and facilitate multi-platform automation within and outside of SAP environments.
Process orchestration
SAP processes are business processes, which means they don’t operate in a vacuum; SAP-related workflows and their outputs must connect and be synchronized with the work of every team and department across enterprise operations. To align and coordinate SAP automations, ensure your chosen solution offers robust process orchestration tools, including a comprehensive suite of capabilities such as intuitive workflow design, plug-and-play integrations and APIs, robust task automation and scheduling, and real-time monitoring and analytics.
Data management and integration flexibility
Seek out core integration capabilities that enable seamless connection to business applications via pre-built packages, sophisticated workflow automation through iPaaS integrations, and support for developers of all skill levels to drag and drop APIs into any process. This is of particular importance for SAP automation, as integrations are necessary to facilitate uninterrupted communication between different systems for efficient data exchange and process automation within SAP and across other applications.
Data privacy controls
An enterprise solution should be able to comply with industry-specific regulations, adhere to GDPR and data privacy principles, including the encryption of sensitive information, and provide essentials-only cloud storage. Essential capabilities to look for include robust encryption methods such as AES-256 for data at rest and SSL/TLS for communication, secure credential storage and management with privileged access management platform integrations, and strict access controls through RBAC and authentication measures like SAML, MFA, and OAuth. Certifications to trust: SOC 1 Type 2, SOC 2 Type 2, ISO 27001, HITRUST, and ISO 22301.
Multi-pronged security
The SAP automation solution you choose should provide robust, multi-tenant, cloud-native environments with data encryption and adherence to privacy compliance. Compliance with major industry data standards and security certifications is essential to ensure data protection. Look for security certifications such as ISO27001 and SOC 1 & 2 Type 2.
SAP automation use cases.
- SAP automation streamlines accounting tasks, including procure-to-pay, invoice capturing, general ledger entries, and reconciliations.
- Automate repetitive tasks such as generating supplier lists, confirming purchase orders, matching invoices, and scheduling payments.
- Ensure accurate financial reporting by automating data-intensive processes such as invoice data validation and transferring entries onto spreadsheets.
- Accelerate complex HR workflows involving multiple systems, data sources, and approvals.
- Automate data collection and manipulation from documents, including benefits forms, vacation requests, and health insurance.
- Streamline and automate repetitive recruit-to-retire processes, including sending interview invites and job offers, screening resumes, and performing background checks.
- SAP automation boosts manufacturing processes throughout the production lifecycle, from planning to QA to restocking.
- Automate inventory management tasks such as material movement, inventory count reconciliation, stock replenishment, and reporting.
- Automate the creation of sales orders and invoices, shipment tracking, updating customer records, and real-time status reporting.
- SAP automation accelerates customer processes, such as issuing payment reminders or requesting documentation for claims or policies.
- Automate backend processes, including resolving claims, formulating quotes, and determining discounts for premiums.
- Streamline every stage of the policy lifecycle from acquisition through renewal or termination.
The evolution of SAP automation.
Automating ERP processes has changed over time to better drive efficiency, innovation, and strategic growth.
Start of ERP Systems
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software began to take form in the 1960s. These early systems were primarily designed for manufacturing and inventory management, helping businesses effectively plan and control complex production processes. Their success paved the way for solutions that would address a wider range of business functions.
Rise of SAP
Thirty years later, SAP emerged as a dominant player in the ERP market. SAP revolutionized the industry, offering a centralized system that integrated disconnected business processes. SAP supported modules for finance, sales, procurement, production, and human resources, providing a comprehensive solution for enterprises to manage their operations efficiently.
Customize and Connect
During the 2000s, ERP systems expanded capabilities to offer highly customizable solutions for specific industries and business needs, integrating business technologies such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems and supply chain management (SCM) solutions. SAP introduced more flexibility and functionality to adapt to unique business processes.
Age of Intelligent Automation
Since the 2010s, the evolution of ERP software has been characterized by the integration of Intelligent Automation and advanced analytics. SAP's introduction of SAP S/4HANA epitomizes this milestone, harnessing in-memory computing for real-time data processing and analytics. At the same time, Intelligent Automation has enabled the automation of routine SAP tasks and enhanced decision-making processes.
Understanding the stakeholders in SAP automation.
As with all enterprise automation projects, SAP automation benefits from engaging a wide array of stakeholders to build robust, transformative, automated processes. A diverse collection of stakeholders—from IT professionals to business analysts and end-users—all play a role in ensuring a broad spectrum of perspectives is considered, leading to more holistic solutions.
SAP automation utilizing an Intelligent Automation platform simplifies this collaborative effort as well as the entire automation lifecycle. A complete AI-powered automation solution enables seamless integration and cooperation among various stakeholders while accelerating the automation lifecycle from process discovery to AI-assisted design to orchestration and continuous performance monitoring while maintaining the core objectives of achieving streamlined and efficient SAP processes.
SAP Automation Specialist
Designs, implements, and maintains automated processes with specific expertise in SAP systems and automation tools.
IT Operations Manager
Oversees IT infrastructure to ensure SAP automation projects align with business goals and IT standards.
Data Analyst
Works closely with SAP automation to analyze data requirements, identify automation opportunities, and oversee data quality and integrity.
Business Process Owner
Defines business requirements for SAP automation in collaboration with business users and other stakeholders to ensure automations meet business needs.
Center of Excellence (CoE)
Enterprise automation team typically comprised of IT personnel, data management experts, and business representatives addressing the interdependence of business, technology, and data.
Subject Matter Experts / Business Users
Brings familiarity with on-the-ground business operations, providing in-context understanding of current processes, helping to elucidate process variations and define rules and goals.
Data Stewards
Responsible for data quality and governance to ensure data manipulation, transformation, and enrichment align with business needs and standards.
Technical SAP Users
Supporting SAP automation specialists with SAP-focused expertise on SAP systems, security, and data integration.
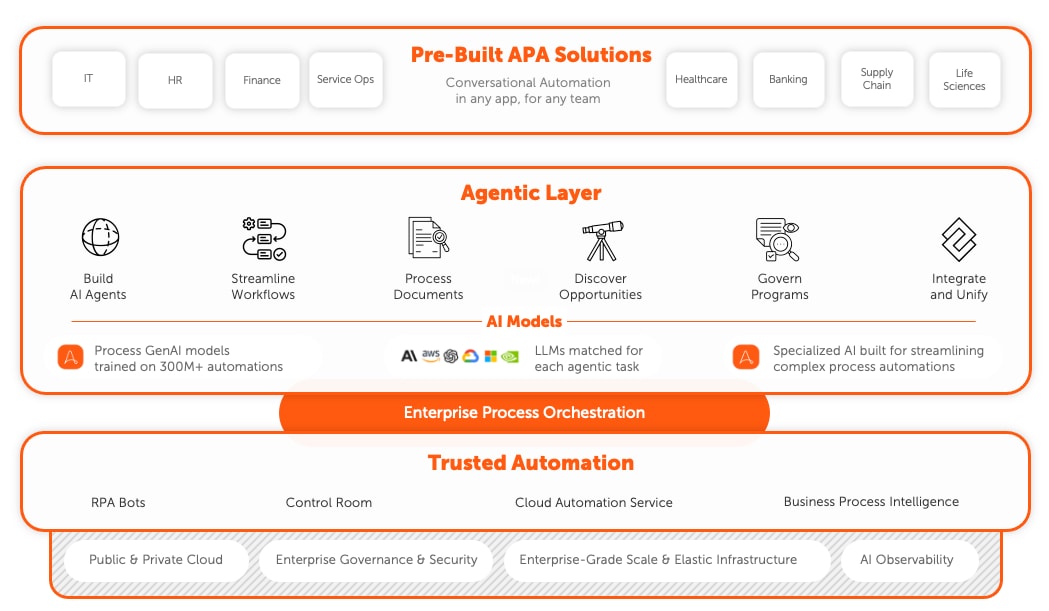
How a complete AI-powered automation platform supports SAP automation.
Achieve successful SAP automation with quick, flexible development and integration by leveraging the Agentic Process Automation System. Get support for the entire automation journey, including workforce management, systems integration, security, and scalability, to enjoy resilient automations, rapid deployment, and effective governance.
Frequently asked questions.
What is SAP?
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) is a company that makes one of the world’s most popular software products for managing business operations and customer relations.
Can SAP be automated?
Yes, SAP business processes can be automated. Some business processes are already automated as part of the platform through the SAP GUI Scripting API. However, Intelligent Automation provides more avenues to automate processes both within SAP applications and between SAP and other applications.
Who can learn SAP automation?
Anyone can learn SAP automation with a wide range of accessible automation tools available on the market. SAP automation can be done through low-code and even no-code interfaces, making it easier to learn than many other technologies.
Is there any business risk to automating?
Risks associated with automating business processes are primarily associated with either human error or platform insecurities. It is essential to automate any business process using only automation technology that offers enterprise-grade security. To mitigate human automation development errors, it is vital to include test management within your automation methodology.
How can SAP automation help businesses?
SAP automation helps businesses by performing time-consuming, repetitive tasks within SAP systems. SAP automation benefits organizations by delivering rapid data access, reducing errors and costs associated with data entry and reconciliations, and strengthening governance and compliance. Some common use cases include automating accounts payable, report creation, and supply chain management processes.
What automations does SAP offer natively?
SAP offers a comprehensive suite of native automation capabilities, including RPA, intelligent document processing, machine learning, and AI, with integration options for partner platforms like Automation Anywhere. This integration allows organizations to incorporate existing automation initiatives seamlessly into their SAP environment. Known for enhanced performance, speed, and deeper integration with SAP systems, SAP's native automation significantly reduces processing times, increases productivity, and provides built-in compliance and security features. It also simplifies maintenance and upgrades, aligns with SAP's development roadmap, and offers scalability and flexibility to meet unique business requirements, maximizing the value of SAP investments.
Why use an automation platform to automate SAP?
Using an automation platform to automate SAP extends the reach of automation efforts by automating beyond standard enterprise processes. An automation platform provides a comprehensive suite of Intelligent Automation tools and enables non-technical stakeholders to visually design and adapt workflows for SAP automation. Top solutions feature built-in AI capabilities for intelligent document processing and generative AI, streamlining automation development both within and outside of SAP without needing specialized data scientist support.
Do you need to know how to code to automate SAP?
No, you do not need to know how to code to automate SAP. With the right automation platform, even non-technical users can design and implement automated processes within and involving SAP applications.
How is SAP Enterprise Automation different from SAP Build Process Automation?
SAP Enterprise Automation is an umbrella term for SAP's holistic approach to automation, encompassing both native automation capabilities and integration with partner platforms such as Automation Anywhere. SAP Build Process Automation is a specific product offering from SAP for automating and orchestrating SAP processes using low/no-code tools.