What is robotic process automation (RPA)?
RPA is technology to create and run business process automations—sometimes called software robots, or "bots"—to automate digital tasks. RPA works by mimicking human actions—like clicking and typing—to navigate and interact with applications and systems via the user interface just as a human would to get work done. Importantly, RPA requires preset rules and logic and structured data inputs, where the format and location of data are consistent across every repetition of the automated process.
What is Intelligent Automation (IA)?
Intelligent Automation, or intelligent process automation (IPA), merges RPA with AI to automate complex processes involving unstructured data, decision-making, and learning. It combines the effectiveness of RPA for well-defined, rules-driven tasks with cognitive tools like ML and natural language processing (NLP) to process documents, interpret and respond to natural language, and even detect and correct errors, enhancing automation resilience and reliability.
Comparing the advantages of RPA vs. Intelligent Automation.
As a rule, automating business processes saves time, reduces errors, and increases efficiency. But applying the right automation tools, whether stand-alone RPA or a holistic Intelligent Automation platform, to the right task can unlock additional benefits from freeing up resources for higher-value, strategic work, to transforming operating models and accelerating growth.
Key benefits of RPA:
- Efficiency and savings: RPA increases efficiency and saves time and costs by automating repetitive tasks.
- Resource allocation: RPA frees human resources for more strategic and value-added work.
- Immediate results: RPA typically requires short implementation time and delivers immediate ROI.
- Accuracy and speed: RPA executes repetitive tasks quickly and without errors, delivering high accuracy at high speed.
Additional benefits of Intelligent Automation:
- Process and data complexity: Intelligent Automation handles complex, end-to-end processes that involve both structured and unstructured data.
- Flexibility at scale: Intelligent Automation can handle the real-world complexity and diversity of business processes, as well as adapt to evolving business conditions and requirements.
- Continuous improvement: Intelligent Automation provides AI-driven insights to improve business decision-making while also continuously improving automation performance through machine learning and feedback.
- Expanded automation footprint: Intelligent Automation enables the automation of more tasks, processes, and workflows, reducing the need for human intervention and enabling operational transformation.
Use cases for RPA and Intelligent Automation by industry.
Finance and accounting use case: Invoice processing
Applying RPA could automate:
- Data extraction: RPA bots extract data from structured invoice forms, such as invoice numbers, dates, amounts, and vendor details.
- Data entry: Bots enter extracted data into the organization’s ERP system.
- Validation: Bots validate the data by applying predefined rules, such as checking if invoice amounts match purchase order amounts.
Intelligent Automation extends the automation to:
- Unstructured data: Intelligent Automation uses AI to extract data from unstructured invoices—e.g. scanned PDFs or images—or where formatting is not consistent.
- Exception handling: Intelligent Automation applies machine learning to recognize patterns and resolve exceptions, such as identifying and correcting invoice amount discrepancies.
- Decision-making: Intelligent Automation uses AI to flag suspicious invoices for potential fraud based on historical data using algorithms for anomaly detection.
Service operations use case: Customer support ticket management
Applying RPA could automate:
- Ticket creation: RPA bots create support tickets by extracting structured data from web forms or emails.
- Routing: Bots route tickets to the appropriate support team based on predefined rules, such as customer-selected issue type or priority.
- Status updates: Bots update on progress by logging ticket statuses in the support system.
Intelligent Automation extends the automation to:
- Natural language processing (NLP): Intelligent Automation uses NLP to analyze unstructured data in customer communications including emails and chat logs to create and categorize support tickets.
- Sentiment analysis: Intelligent Automation applies sentiment analysis to prioritize tickets based on customer sentiment.
- Automated responses: Intelligent Automation uses AI to generate automated responses to common questions.
Banking & financial services use case: Loan application processing
Applying RPA could automate:
- Data collection: RPA bots collect structured data from loan application forms, such as applicant details, income, and loan amount.
- Initial screening: Bots perform initial screening by checking applicant data against predefined criteria, such as credit score thresholds and income requirements.
- Document upload: Bots upload necessary documents to the document management system.
Intelligent Automation extends the automation to:
- Document processing: Intelligent Automation uses AI to analyze unstructured documents—e.g. bank statements and tax returns—to extract relevant financial information.
- Risk assessment: Intelligent Automation applies machine learning models to assess loan application risk, considering more complex factors such as spending patterns and financial stability.
- Automated decision-making: Intelligent Automation provides application approval or rejection recommendations to underwriters.
Human resources use case: Employee onboarding
Applying RPA could automate:
- Form filling: RPA bots fill out structured onboarding forms with employee details, such as personal information, job title, and start date.
- Account creation: Bots create user accounts in workplace applications and systems of record, such as email, HR software, and access control systems.
- Notification: Bots send welcome emails and notifications to managers and departments about the new hire.
Intelligent Automation extends the automation to:
- Document verification: Intelligent Automation uses AI to verify new hire documents, such as identification, certifications, and employment contracts.
- Personalized onboarding: Intelligent Automation supports personalized onboarding experiences by analyzing prior experience and role requirements to plan training programs and resources accordingly.
- Compliance tracking: Intelligent Automation ensures mandatory compliance training and documentation are completed and tracked, sending reminders and updates to both new hires and HR managers.
Manufacturing use case: Supply chain management
Applying RPA could automate:
- Order processing: RPA bots automate the processing of purchase orders, extracting structured data from order forms and entering it into the supply chain management system.
- Inventory updates: Bots update inventory levels in real-time as orders are processed and fulfilled.
- Shipment tracking: Bots track shipments and update status information in the logistics system.
Intelligent Automation extends the automation to:
- Demand forecasting: Intelligent Automation uses AI to analyze historical sales data, market trends, and external factors like weather and economic indicators to predict demand.
- Supplier management: Intelligent Automation applies machine learning to evaluate supplier performance and optimize supplier selection based on quality, cost, and reliability.
- Predictive maintenance: Intelligent Automation uses AI to predict equipment failures and schedule proactive maintenance.
Evolution of automation software from RPA to Intelligent Automation and beyond.
Productivity on repeat
Automation technology has come a long way from its early days, where IT and business analysis teams streamlined manual processes through basic scripting and macros, providing significant, if limited in scope, efficiency gains. But these fledgling automations, coupled with the development of better optical character recognition (OCR) tools, whet enterprise appetites for more robust and easy-to-use automation solutions. Within this context, robotic process automation (RPA) emerged, enabling organizations to quickly and reliably automate mundane, repetitive, rule-based tasks. RPA bots could work like humans by interacting with various software applications through their user interfaces to execute work tasks such as data entry, form filling, report generation, and transaction processing. RPA on its own created a step-change in productivity and accuracy, particularly in back-office operations, freeing human workers to focus on more value-adding, strategic, and creative tasks.
Conquering complexity
At the same time as the limitations of RPA were becoming more apparent in the face of increasingly complex enterprise processes involving unstructured data and rapid decision-making, cognitive automation technologies in the form of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) tools were coming into their own. This led to the evolution of Intelligent Automation—a force multiplier combining RPA with AI to extend enterprise automation capabilities to end-to-end processes that require cognitive processing and adaptive learning. Joining forces with intelligent document processing (IDP), Intelligent Automation can work with unstructured data, perform advanced analytics, and make data-driven decisions. This evolution has allowed organizations to automate not only routine tasks but also complex workflows, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and driving digital transformation.
Hello, Generative AI
The current evolution of automation technology is being driven by generative AI, a subset of AI that can create new content and generate near-instant insights from large datasets. Infusing Intelligent Automation with the power of generative AI is transforming automation, enabling never-before-seen flexibility, accelerating the entire automation development lifecycle, and opening the door to new and creative use cases. For instance, in healthcare, generative AI can revolutionize patient care by analyzing vast amounts of medical data to generate personalized treatment plans and predict patient outcomes. Additionally, it can assist in drug discovery by simulating various molecular combinations and predicting their efficacy. In customer service, generative AI can enhance chatbots by enabling them to generate personalized responses and provide deeper insights into customer behavior.
Agentic automation
The next evolution of Intelligent Automation is already taking shape in the form of AI agents and agentic automation. AI agents are entities that combine the power of large language models (LLMs) and generative AI with the ability to take responsible action across applications and environments. Agentic AI is a term used to refer to this form of artificial intelligence. Agentic automation, as well as Agentic Process Automation, involve harnessing intelligent AI agents to create adaptive, self-improving systems with the potential to significantly enhance operational flexibility, efficiency, and innovation. The convergence of generative AI capabilities with Intelligent Automation is expected to define a new generation of adaptive, intelligent, and efficient automation systems.
Choosing the right automation path for your business process.
The wide range of comprehensive automation solutions available means that it’s rarely necessary to choose strictly between RPA and full-scale Intelligent Automation. Rather, business process automation involves selecting the right automation tools to apply for each process or workflow. A robust evaluation of process attributes and operational requirements helps to determine your automation success path to achieve business goals.
Repetitiveness
Evaluation criteria
What is the frequency and volume of performing the task/process?
RPA applicability
High-frequency/volume repetitive processes are ideal candidates for RPA.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Medium to high frequency/volume processes are ideal candidates for Intelligent Automation.
Logic
Evaluation criteria
To what degree does the task/process follow a set of predefined rules or conditions?
RPA applicability
Highly defined processes are a fit for RPA.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Both less-defined and highly defined processes are candidates for Intelligent Automation.
Data structure
Evaluation criteria
What type(s) of data are used in the process (structured vs. unstructured)? Does the data need to be extracted, transformed, or processed?
RPA applicability
If structured data is available, RPA is a fit.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Any data inputs, including unstructured data requiring extraction and transformation, are a fit for Intelligent Automation.
Complexity
Evaluation criteria
What is the level of complexity in the process? E.g. What is the number of steps and decision points?
RPA applicability
Any number of steps, fewer decision points, is best fit for RPA.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Any number of steps and decision points is a fit for Intelligent Automation.
Accuracy/Error rate
Evaluation criteria
What is the current accuracy requirement or target and/or error rate of the process?
RPA applicability
RPA can deliver high accuracy.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Intelligent Automation can deliver high accuracy.
Scale
Evaluation criteria
Is the process expected to increase in volume or frequency over time?
RPA applicability
RPA can scale effectively for static, consistent processes.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Intelligent Automation can scale effectively for processes with varying degrees of change over time.
Applications/system integrations
Evaluation criteria
How many applications/systems/databases does the process involve?
RPA applicability
RPA is ideal for interacting via user interfaces.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Intelligent Automation is designed for multiple connection types/integrations.
Human in the loop
Evaluation criteria
To what extent does the task or process involve human intervention or oversight?
RPA applicability
RPA can support simple human-in-the-loop requirements.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Intelligent Automation can support complex human-in-the-loop workflows.
Customer facing
Evaluation criteria
Does the process directly impact/interact with customers or other external parties?
RPA applicability
RPA may be too rigid for customer interactions, but can deliver high accuracy for predetermined processes that support customer needs.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Intelligent Automation can be flexible and accurate enough to interface directly with customers.
Dependencies
Evaluation criteria
Are there dependencies between different tasks and processes within the workflow?
RPA applicability
RPA is ideal for low-dependency workflows.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Intelligent Automation is designed for any number of workflow dependencies.
Dynamics/change
Evaluation criteria
What is the level of change over time expected for the process? Will the process need to adapt quickly to changes in business requirements?
RPA applicability
RPA works best for static processes.
Intelligent Automation applicability
Intelligent Automation is flexible and adaptable, even automatically, to process changes over time.
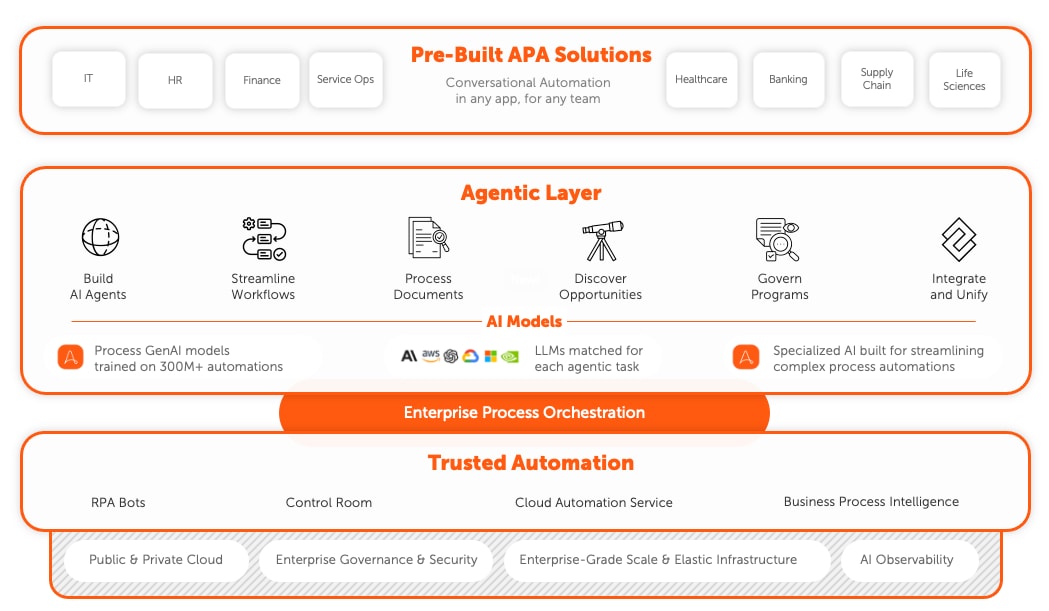
Get started with the complete AI + Automation Enterprise System.
Get support for the entire Intelligent Automation journey—and beyond—including workforce management, systems integration, security, and scalability. Achieve out-of-the-gate automation success with resilient AI-powered automations, rapid deployment, and effective governance.
Frequently asked questions.
What types of businesses benefit the most from IA?
All types of businesses can benefit from Intelligent Automation (IA), but enterprises with complex, data-intensive processes see the most significant gains from implementing the technology. In industries such as healthcare, finance, insurance, manufacturing, and retail, the need to handle unstructured data and automate end-to-end workflows involving multiple enterprise systems and integrations makes Intelligent Automation particularly beneficial.
What are the security considerations for RPA and IA?
Both RPA and Intelligent Automation (IA) come with security considerations that must be addressed to ensure the integrity, privacy, and safety of data and systems:
For RPA, security considerations include access controls, data encryption, and ensuring that bots only have application permissions that are strictly necessary to perform their tasks. Monitoring RPA bot activities and maintaining audit trails to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches are core RPA security requirements.
Over and above RPA security requirements, Intelligent Automation requires robust protection for AI models and data used for machine learning. This includes securing data pipelines, protecting AI algorithms from tampering, and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations. In addition, audits and usage monitoring are needed to protect against external threats and potential misuse.
How do IA and RPA impact job roles and employment?
Technologies like robotic process automation (RPA) and Intelligent Automation (IA) are central to the Fourth Industrial Revolution and Automation Economy that are reshaping the workforce, creating new opportunities while also posing challenges that require a strategic approach to workforce development and management.
RPA technology is typically used to automate repetitive tasks, freeing employees from mundane work to focus on more strategic, creative, and value-adding activities, which can lead to better employee experience and role enhancements rather than reduced headcount. For instance, administrative staff can shift time from data entry to more customer-centric work, improving service quality and customer satisfaction.
Intelligent Automation extends the workforce benefits of RPA by automating more complex tasks and decision-making processes. At the same time, Intelligent Automation is part of the bigger picture of job role evolution/disruption, as new technologies both create opportunities and job categories, such as data scientists, AI specialists, and automation strategists, as well as displace some traditional job roles. Reskilling and upskilling within a culture of continuous learning and innovation are central to adapting workforces to technology-driven change, ensuring that both technology and human talent are used to the best of their potential.
What skills are required for managing IA and RPA workflows?
Managing RPA workflows starts with understanding business processes and having strong problem-solving skills. From a technical perspective, managing RPA workflows typically requires skills in process analysis, basic programming (e.g. scripting), and familiarity with RPA tools and platforms.
Overseeing Intelligent Automation programs involves additional business skills in project management, change management, and an understanding of ethical AI practices. Building and managing Intelligent Automation workflows also requires a broader technical skill set, including knowledge of AI frameworks, model training, and data preprocessing, data analysis, and advanced programming languages.
Can IA and RPA work with legacy systems?
Yes, both Intelligent Automation (IA) and RPA can work with legacy systems. One of the advantages of RPA is its ability to interact with legacy systems through the user interface following the same steps as humans use to interact with the applications, allowing organizations to automate processes without developing custom integrations or system changes.
In the same way, Intelligent Automation can integrate with legacy systems using RPA as a bridge, while also applying AI capabilities for better data extraction, processing, and analysis. Additionally, Intelligent Automation is designed to employ APIs and other integration tools to connect with legacy systems for faster and more seamless automation across different technology environments.