The value of AI agents to enterprise operations.
With the ability to handle intricate cognitive tasks, including making decisions in real time, AI agents can accelerate complex processes while working autonomously within dynamic business environments.
Deliver
more effective and efficient service with error-free execution of complex and sensitive service tasks like responding to inquiries.
Ensure
compliance and responsible use of AI when implemented with built-in security and governance to set guardrails and provide full traceability.
Accelerate
business operations with responsible, autonomous execution of cognitive work and end-to-end business processes.
Drive
competitiveness with faster and more flexible automation of business processes that target desired outcomes rather than step-by-step progression.
Power
productivity by augmenting and accelerating the effectiveness of your human workforce with AI-powered assistants.
Defining features of AI agents
Distinct from automation technologies like robotic process automation (RPA) bots, it is possible to identify AI agents by their characteristics including the ability to learn from their environment and take action.
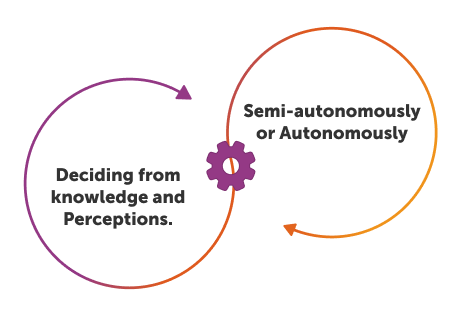
Purpose-driven
AI agents are built around predefined objectives rather than process steps. They work towards an assigned goal using all of the capabilities and information available to them, such as enterprise knowledge and perceptions from their environment.
Planning
AI agents work toward their objective by planning or creating action sequences. AI agent planning capabilities have significantly advanced with the integration of LLMs.
Autonomy/Partial autonomy
AI agents can operate without direct human involvement or intervention. They can make decisions and act on their own to achieve their goal.
Perception
AI agents perceive and process new information as it happens. Leveraging sensors and/or data inputs, they can evaluate their operating environment and adapt their actions accordingly.
Memory
AI agents store their plans, experiences, and interactions to enable the continuity of their work, inform future actions, and improve their performance.
Reasoning
AI agents can make decisions and solve problems. Based on their perceptions of the environment or situation, by processing new information and relating perceptions to their foundational knowledge and defined goals, AI agents can choose the best course of action.
Learning
AI agents learn from data inputs and experiences. Harnessing machine learning (ML) algorithms to improve their performance, AI agents can increase their accuracy and effectiveness over time.
Action
AI agents can take action. Connected to actuators and systems of execution such as ERP applications, AI agents can interact with and affect their environment to achieve assigned goals and objectives.
Types of AI agents.
The diversity of AI agent types reflects the need to execute an infinite variety of cognitive tasks across industries and environments. Each type of AI agent, from simple reflex to hierarchical, has unique strengths and attributes that make them suitable for different enterprise automation scenarios.
AI agent categorization is based on traits such as reactivity or proactivity, the nature of their environment, and whether they operate alone or as part of multi-agent systems. For example, static environments may require responsive task execution, while dynamic interactions will require AI to learn and adapt.
Understanding the standard types of AI agents and their applicability provides essential background to the AI-powered automation landscape.
Simple reflex agents
Reactive, basing their actions on preset rules and current data or cues only, simple reflex agents work well for simpler cognitive tasks that require immediate response without extensive reasoning. For example, to reset customer passwords when specific keywords are detected in a conversation. Or for smart homes, to adjust the temperature based on thermostat data.
Model-based reflex agents
Using an internal model built on data inputs and perceptions, model-based reflex agents make informed decisions that require context outside of immediate task data, making them effective for more complex tasks that involve predicting outcomes. For example, suggesting driving routes using maps and location updates.
Goal-based agents
Taking rules to another level, goal-based agents apply reasoning to weigh different paths to achieving a specific outcome in order to choose the most efficient approach. For example, these agents can help with scheduling tasks that must conform to certain deadlines or parameters.
Learning agents
As their name implies, learning agents continuously evolve and improve performance based on experiences and collected data. This capacity to adapt is suited to tasks such as recommendation engines that more closely reflect user preferences as they learn from feedback and interactions.
Rational/utility-based agents
Designed to assess options for optimal resource allocation or maximum overall outcome based on utility values or benefits, utility-based agents make decisions that align with user preferences and goals. For example, scaling computing resources based on application needs to optimize for performance and costs.
Hierarchical agents
Like managers, hierarchical agents deconstruct complex tasks into smaller ones and assign them to subordinate task-specific agents. The higher-level agent collects the results and coordinates agents to ensure the collective achievement of goals.
Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
Consisting of numerous interacting agents with varying levels of autonomy, multi-agent systems coordinate/compete and communicate with each other to achieve shared objectives. MAS are ideal for solving intricate problems and boosting efficiency in diverse applications.
Responsible use, security, and governance of AI agents.
Incorporating AI agents into enterprise automation demands safeguards to ensure responsible use, data privacy, and security. Responsible AI deployment is increasingly crucial to maintaining the trust and reliability of business operations.
Responsible Use
Responsible deployment of AI agents requires transparency in their implementation and actions. Defining the scope and constraints within which agents operate can help prevent misuse while also ensuring their actions align with organizational values and standards. AI agent platforms should include visibility and traceability across agent interactions and activity to enable regular audits. Maintaining updated AI systems also supports agent performance as intended.
Data Privacy
Safeguarding sensitive information requires implementing frameworks to ensure stringent data governance. AI agents can support privacy compliance by following relevant regulations such as GDPR or CCPA and by applying data anonymization techniques such as masking to scrub PII or other sensitive information from inputs. Limiting data access to necessary information only is another lever to mitigate risk and enhance privacy protection.
Security
Similar to any enterprise AI and automation deployment, security is a core requirement for the safe implementation of AI agents. This involves using advanced encryption to protect data in transit and at rest, as well as securing all access points. Regular security assessments and penetration testing are essential to identify vulnerabilities. Stored data should be shareable with integrated security and event management (SIEM) platforms. Platforms should employ multi-factor authentication and maintain updated and robust cybersecurity infrastructure to defend against security threats.
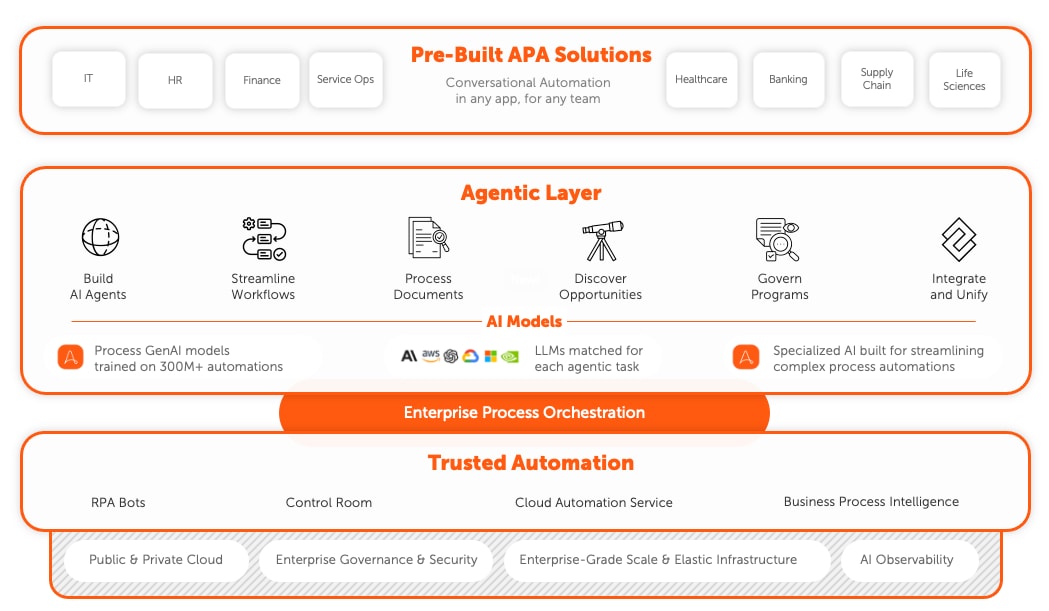
What to look for in an agentic automation platform.
Effective AI agents connect with enterprise architecture to work with your AI models, enterprise applications and systems, and across environments. Open, flexible agentic automation platforms offer easy agent creation with seamless integration of AI to perform cognitive tasks alongside stringent security and governance capabilities to ensure safe, responsible AI deployment across enterprise data, systems, and processes.
No-code agent creation
Building AI agents should not require data science expertise. Look for solutions that empower business users (and accelerate developers) with templates and an intuitive agent creation experience.
LLM choice and customization
LLM choice is a significant factor in designing effective AI agents. Grounding in enterprise knowledge enables agents to match the way your business operates for better results, faster. Effective solutions will connect with any large language model (LLM) and enable customization based on enterprise data.
AI skills
AI agents can be made with specific skills to execute business tasks. Skills represent sets of generative AI prompts that are linked together. Look for platforms that facilitate rapid agentic automation by packaging sets of generative AI capabilities into reusable AI skills that others can use for faster agent development.
Integration
As the name implies, agentic automation requires the ability to seamlessly integrate generative AI into automation workflows. Embedding generative AI within automations is the key to enabling AI agents to execute cognitive tasks at scale. The security and compliance framework provided by AI-powered automation platforms will determine the safety and compliance of deploying AI agents. Identify providers that offer integration flexibility via open architecture alongside robust platform security and both AI and automation governance features.
Multi-agent orchestration
AI agents should be able to team up across mission-critical enterprise processes and be integrated into your enterprise architecture. To align and coordinate AI agents, ensure your chosen solution offers robust process orchestration tools and multi-agent orchestration features. Look for a comprehensive suite of capabilities that include intuitive workflow design, plug-and-play integrations and APIs, robust task automation and scheduling, and real-time monitoring and analytics.
AI governance
Full visibility into every AI activity and response is necessary to enforce responsible AI policies and protect company data. Enterprise solutions will enable you to set guardrails for consistent use and human validation, review content within prompts and model responses for sensitivity and relevance, and monitor and audit both agent and model performance. Logs and analytics for both prompts and model responses should feed insights into model performance and accuracy.
Data privacy controls
An enterprise agentic automation solution will be able to comply with industry-specific regulations, adhere to GDPR and data privacy principles, including the encryption of sensitive information, and provide essentials-only cloud storage. Essential capabilities to look for include robust encryption methods such as AES-256 for data at rest and SSL/TLS for communication, secure credential storage and management with privileged access management platform integrations, and strict access controls through RBAC and authentication measures like SAML, MFA, and OAuth. Certifications to trust: SOC 1 Type 2, SOC 2 Type 2, ISO 27001, HITRUST, and ISO 22301.
Multi-pronged security
The agentic automation solution you choose should provide robust, multi-tenant, cloud-native environments with data encryption and adherence to privacy compliance. Compliance with major industry data standards and security certifications is essential to ensure data protection. Look for security certifications such as ISO27001 and SOC 1 & 2 Type 2.
Use cases for AI agents by business function and industry.
- Journal entries and reconciliations:
AI agents can accurately capture and centralize transactions in real time across departments. - Invoice processing:
AI agents can execute invoice processing from matching invoices to purchase orders through to payment. - Financial reporting and audit:
AI agents can review documents and continuously monitor financial data to assist auditors in creating accurate data financial reports.
- Onboarding:
AI agents can deliver expert knowledge and workflow assistance in real time within the applications where service employees are working. - Predictive maintenance:
AI agents can monitor equipment and systems, predicting potential failures and initiating proactive response measures to minimize downtime and costs. - Customer support:
AI agents equipped with NLP can respond to customer inquiries around the clock to reduce wait times and accelerate inquiry resolution.
- Network monitoring and anomaly detection:
AI agents can monitor network traffic for unusual patterns or anomalies that could signal a security threat. - Security threat response:
AI agents can isolate devices or initiate countermeasures as defined by InfoSec protocols. - Help desk automation:
AI agents can autonomously resolve common requests such as resetting passwords or provisioning new devices.
- Claims processing:
AI agents can automate claims routing and execute real-time loss assessments by leveraging sensor data from IoT devices. - Underwriting:
AI agents can analyze large volumes of data in real time to create accurate quotes. - Fraud detection:
AI agents can look for patterns and anomalies to detect fraud risks and stream authentic claims for faster processing.
- Accurate diagnostics:
AI agents can precision-analyze medical images (X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans) using advanced image recognition algorithms to expedite diagnosis and improve the identification of abnormalities. - Personalized treatment plans:
AI agents can harness diverse datasets (patient history, genetics, treatment outcomes, etc.) to generate personalized plans that minimize potential side effects. - Workflow optimization:
AI agents can reduce the administrative burden on healthcare professionals by assisting with routine yet complex work such as documentation processes.
- Issue resolution:
AI agents can apply predefined scripts, enterprise knowledge, and machine learning algorithms to efficiently handle a broad range of customer inquiries and issues. - Multichannel service:
AI agents can integrate with multiple communication platforms (websites, mobile apps, social media) to provide unified service to customers across channels. - Recommendations:
AI agents can generate and communicate tailored product recommendations based on customer data such as browsing history and purchase behavior.
How do AI agents work?
AI agents are typically built on large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 and interact with users via prompts. They use long-running memory to maintain and understand context and learn dynamically in real time. AI agents can interact with services and tools to take action and accomplish their objectives. They operate—and cooperate, via multi-agent orchestration—across enterprise systems and functions, eliminating automation siloes.
While AI agents have different skill sets to operate in diverse settings, from self-driving cars to healthcare, their workflow to execute complex cognitive tasks in an enterprise context includes a set of common components, reflecting the characteristics that make AI agents distinct from other applications of AI technologies.
Perceiving
Assessing their operating environment by perceiving and interpreting information from all available sources, such as sensors or cameras, as well as direct data inputs, such as user prompts.
Defining goal/objective
Synthesizing the data and input perceived to identify and establish clear objectives or goals and define what needs to be achieved.
Acquiring information
Researching and gathering relevant information from available sources, such as knowledge bases/databases, the internet, and interactions with humans, to inform the planning and decision-making process.
Reasoning, planning, and decision-making
Working with acquired information, applying algorithms and models to reason through potential execution paths to determine how to progress toward their goals.
Action/execution
Progressing toward desired outcomes by acting on decisions using actuators or software interfaces to execute digital/physical tasks.
Learning and adaptation
Carrying experiences, feedback, and outcomes forward to apply to future tasks through memory and applying learning models to adapt strategies and behaviors for effectiveness, efficiency, and overall performance.
Trends shaping the future of AI agents.
No-code agent customization
Creating custom AI agents is quickly becoming faster and easier—and accessible without data science expertise. Until recently, building AI agents and agentic automations required expert-level AI developers to connect LLM capabilities with custom-built code to create a unified agent. The nuances and sensitivities of designing and testing LLM prompts represented a significant barrier to development. However, today, new no-code tools to build AI agents are quickly transforming the landscape, bringing agent creation to business users with prebuilt model connectors, the ability to easily add human-in-the-loop, and built-in safety guardrails.
Agent-to-agent ecosystems
The application of AI agents for business is moving towards multi-agent and agent-to-agent systems. Harnessing systems of linked agents represents a major opportunity for organizations to achieve greater efficiency and collaboration by deploying AI technology. These systems are characterized by communication and coordination between multiple AI agents, driving seamless decision-making for accelerated autonomous operations with optimal resource allocation. By breaking down complex objectives into components that leverage the specific capabilities of individual AI agents, multi-agent systems can orchestrate AI-powered automation across enterprise operations. New advancements in agent-to-agent interactions are enabling collective problem-solving among interconnected AI agents, allowing them to navigate complex business ecosystems both within and between organizations.
Governance and responsible AI
Agentic AI and AI technologies have already proven their transformative potential across industries. As businesses embrace and accelerate the development and deployment of AI agents, governance frameworks, ethical considerations, and the nature of regulatory oversight are evolving topics with far-reaching relevance for enterprises. Collaborative efforts at the global level seek to address wide-ranging issues such as verifiable honesty, data protection, transparency, access, and misuse, as well as the need for agile governance and strategic oversight of multi-agent systems. As new standards for governance and responsible AI are defined, they will shape the next wave of AI advancements and their business applications. Implementing agentic automation grounded in accepted governance frameworks and ethical guidelines will establish trust and enable long-term success.
How a complete AI-powered automation platform supports AI agents.
Create and deploy resilient, responsible agentic automations with effective governance and support for the entire automation journey, including workforce management, systems integration, security, and scalability.
Frequently asked questions.
What are the challenges and limitations of AI agents?
Challenges and limitations of AI agents are similar to those surrounding the implementation and effectiveness of working with AI technologies in general. These include:
- Bias and interpretability: Complex AI models rely on training data and inputs that may be biased or incomplete. At the same time, the behavior of AI models is difficult to explain, compounding the challenge of identifying and mitigating bias.
- Ethics and regulatory uncertainty: Ongoing global discussions about privacy, fairness, accountability, and potential misuse are indicators of the complexities and sensitivities inherent in the application of AI technologies. The rapid advancement of AI technology has outpaced regulatory frameworks, leading to uncertainties around legal implications, accountability, and compliance requirements.
- Common sense/contextual understanding: AI agents can struggle to understand context due to AI challenges with common sense reasoning. While making judgments based on implicit knowledge and common sense understanding is something humans develop over time, AI does not automatically acquire the same skills.
How do AI agents differ from traditional agents?
Compared to traditional automated agents, AI agents differentiate in their abilities to perform cognitive tasks. AI agents have several key traits that set them apart:
- Learning: AI agents can learn and adapt based on data inputs and perceptions from their environment/interactions, while traditional agents execute tasks based on programmed rules and instructions.
- Autonomy: AI agents can make decisions and take actions without human direction, while traditional agents must follow prescribed steps and wait for human decisions to initiate next steps.
- Complexity: AI agents harness generative AI models and machine learning to tackle complex and ambiguous data and interactions. In contrast, traditional agents rely on pre-structured information and workflow logic.
Can AI agents work collaboratively with human teams?
Yes, AI agents can work cooperatively and collaboratively with human teams by handling adjacent workflows or data analysis to augment human-driven work. For example, in a service operations setting, AI agents and Agentic Process Automation can accelerate human agent effectiveness by surfacing expert-level knowledge and workflow assistance relevant to the call or task, and personalized to the customer. It is important to deploy AI agents within a secure automation framework to facilitate safe collaboration and integration into existing workflows.
What is the difference between supervised and unsupervised learning in AI agents?
Supervised and unsupervised learning are core techniques for training AI. AI agents use both supervised and unsupervised learning to acquire knowledge and learn how to make decisions.
- Supervised learning in AI agents: This forms the knowledge base of the AI agent, where it can draw on prelabeled data with examples of problems and solutions. For example, a customer service AI agent may refer to its knowledge base for applicable scenarios and resolution paths. Supervised learning is defined by the scope of these data inputs, potentially limiting agents' effectiveness when they face new problems that diverge from their existing knowledge.
- Unsupervised learning in AI agents: This type of learning provides AI agents with information that isn't associated with predefined problems and outcomes. The agent must learn to find solutions by reviewing its past actions and experiences, giving the agent the ability to problem solve as it encounters new tasks, even if it has never seen them before. Unsupervised learning helps AI agents become adaptive and flexible.
How do AI agents handle conflicting objectives or goals?
Different types of AI agents are more or less suited to different kinds of tasks. Handling conflicting goals or objectives is best suited to utility agents. Utility agents aim to maximize overall satisfaction. Utility agents assess courses of action by evaluating the relative utility associated with their expected outcomes. This type of agent is effective when facing conflicting goals or multiple courses of action can be taken without a single best approach.
How can businesses measure the effectiveness of their AI agents?
Measuring AI agent effectiveness falls into two categories: AI performance and business KPIs.
For developers and automation leaders, AI agents can be evaluated during development and testing for by assessing task performance, accuracy in multi-step scenarios, progression toward successful outcomes, task completion, success rate, and reversed redundancy ratio (RRR) which measures the efficiency of task completion.
Business teams can assess the impact of AI agents and their level of effectiveness by establishing benchmarks for tasks and processes and comparing AI agent-assisted or AI agent-driven outcomes against them. Standard business process KPIs such as accuracy, efficiency, and cost savings, are go-to metrics for measuring AI agent impact.
How do AI agents manage and store data?
AI agents manage and store data according to the data handling rules of their underlying models and technologies. Data storage and retrieval are central to AI agent effectiveness, since they must access, process, reference, and create data as they work.
AI agents my use some of the following data management and storage approaches:
- Databases: AI agents store structured data in database format for efficient retrieval, analysis, and updates. Popular databases include relational databases like MySQL, NoSQL databases like MongoDB, and in-memory databases like Redis.
Data Lakes: For large volumes of unstructured and semi-structured information, AI agents may use data lakes which provide access to vast information stores for analysis and modeling.
Cloud Storage: Offering scalable and secure storage, with high availability for AI applications, cloud storage services such as Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Microsoft Azure Storage are popular data stores for AI agents. - Data Warehouses: AI agents may use data warehouses with optimal querying capabilities to store and manage large volumes of structured data for analytics.
- Distributed File Systems: AI agents use distributed file systems like HDFS and S3 to store and process large datasets across multiple nodes in a distributed environment, enabling parallel processing and fault tolerance.